Fig. 1.
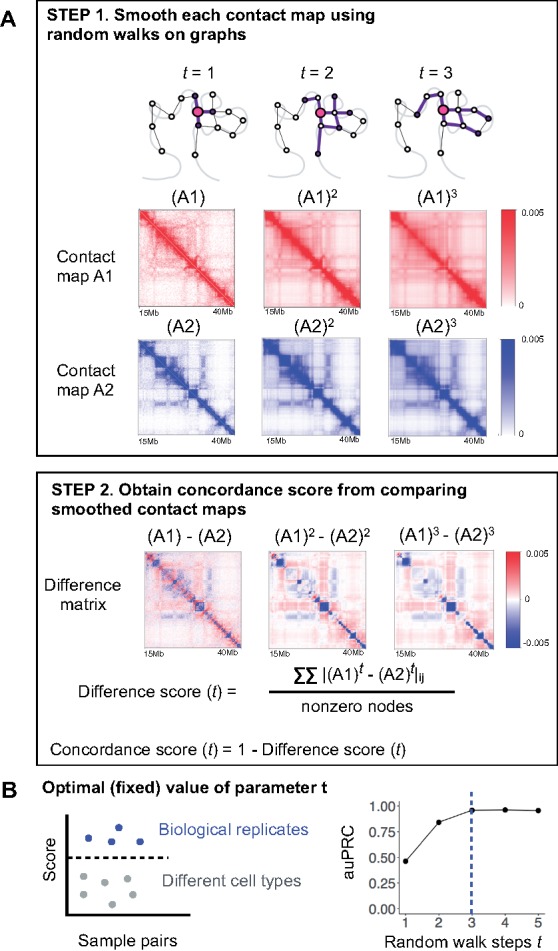
Overview of GenomeDISCO. (A) GenomeDISCO consists of two steps. The first step in comparing two contact maps, and , consists of smoothing each contact map using random walks. Depicted are the smoothed contact maps, at different levels of smoothing controlled by the parameter , which specifies the number of steps of random walk used for denoising. The second step consists of computing a difference score between the smoothed contact maps, as a function of . (B) Procedure for identifying the optimal value for . We computed concordance scores for pairs of samples that are either biological replicates from the same cell type or pairs of samples from different cell types. We assume that the optimal value of will produce scores that can accurately classify pairs of samples into ‘biological replicates’ and ‘different cell types’. For each value of , we measure classification performance using the auPRC, finding =3 to be optimal
