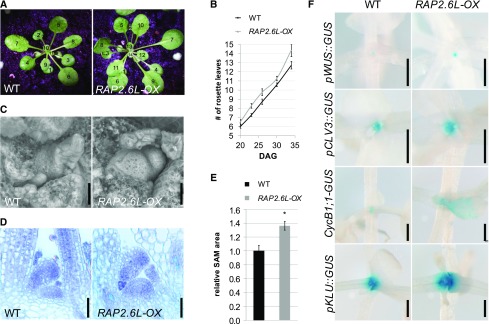
Figure 2.
RAP2.6L-OX plants show amp1-related vegetative phenotypes. A, Wild-type Col-0 (WT) and RAP2.6L-OX plants grown under short-day conditions for 34 d. Leaves are numbered in the consecutive order of appearance. B, Quantification of rosette leaves in wild-type Col-0 (WT) and RAP2.6L-OX plants at the indicated time points grown under short-day conditions (values represent means ± se; n ≥ 8). C, Scanning electron micrographs of SAM areas of wild-type Col-0 (WT) and RAP2.6L-OX seedlings grown under short-day conditions for 18 d. D, Median longitudinal SAM sections of wild-type Col-0 (WT) and RAP2.6L-OX seedlings grown under short-day conditions for 18 d. E, Quantification of SAM area from median longitudinal sections of wild-type Col-0 (WT) and RAP2.6L-OX seedlings. Normalized values (wild type = 1) are shown (bars represent means ± se; n ≥ 3). Asterisk indicates a significant difference (Student’s two-tailed t test; P < 0.05). F, Comparison of GUS activities of the indicated reporter lines in wild-type and RAP2.6L-OX seedlings grown under short-day conditions. Plants were analyzed at 15 DAG except for pWUS::GUS (18 DAG). Bars = 25 μm (C and D) and 500 μm (F).