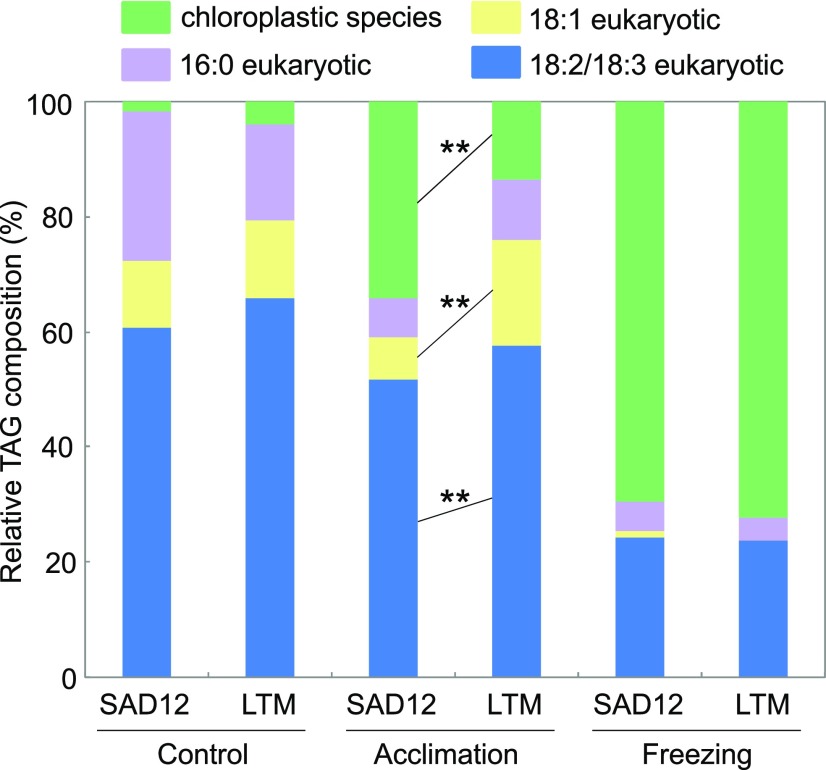
Figure 8.
Relative molecular species compositions of TAG in B. stricta SAD12 and LTM seedlings subjected to control conditions, cold acclimation, or cold acclimation followed by freezing. TAG classes indicated by different colors were characterized by distinctive acyl chain compositions. Chloroplastic species contained 16:3, indicative of a galactolipid precursor. Based on a χ2 test, overall relative TAG molecular species compositions in control conditions and in response to freezing were similar, but TAGs formed during cold acclimation differed (P < 0.01). Three groups of TAG molecular species formed during acclimation showed ecotypic differences, as indicated by asterisks (**P < 0.01, n = 5–6; ANOVA).