Figure 7.
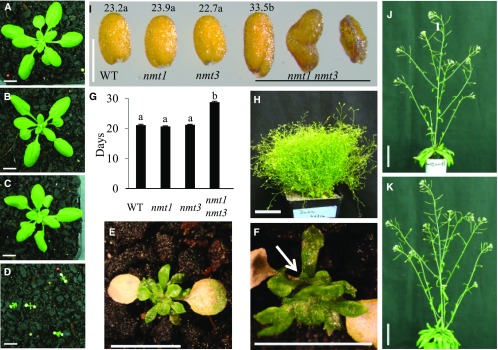
Loss of NMT3 in an nmt1 background severely compromises aerial growth and reproduction through choline deficiency. A to D, Representative rosettes of 3-week-old soil-grown wild type (A), nmt1 (B), nmt3 (C), and nmt1 nmt3 (D) plants. Bars = 1 cm. E, Enlarged view of a 3-week-old nmt1 nmt3 rosette. Bar = 0.5 cm. F, Side view of E. The white arrow points to a secondary rosette. Bar = 0.5 cm. G, Days to bolting in wild-type (WT), nmt1, nmt3, and nmt1 nmt3 plants under a 16-h photoperiod. Values are means ± se (n = 11–88). Statistical significance tested by one-way ANOVA is denoted by different letters above the bars (P < 0.05). H, Sixteen-week-old reproductive nmt1 nmt3 plant. Bar = 5 cm. I, Photograph of representative wild-type, nmt1, nmt3, and nmt1 nmt3 mature seeds. Wild-type, nmt1, and nmt3 seeds were of similar color, size, and shape. nmt1 nmt3 seeds fell in three visually and morphologically distinct groups, from left to right: full seed, shrunken seed, and aborted seed (see text). Numbers above seeds are mean dry weight per seed (ng; se = 0.9, 1, 0.6, and 0.9, respectively; n = 80–110 seeds). For nmt1 nmt3, only the mean dry weight of the few morphologically normal seeds is shown. Values topped by the same letter were not significantly different by one-way ANOVA (P < 0.05). Bar = 0.5 cm. J and K, Five-week-old nmt1 nmt3 (J) and wild-type (K) inflorescences under choline feeding. Plants were sprayed daily with 2 mm choline, starting from 4 d after cotyledon emergence. Bars = 5 cm.