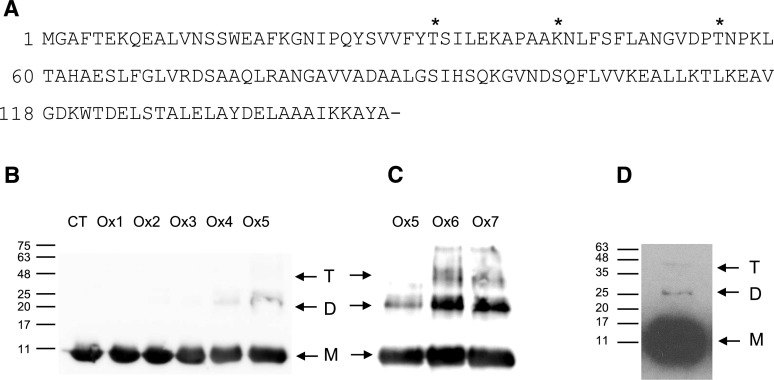
Figure 5.
Carbonylation of bean nodule Lb. A, Amino acid sequence of Lb in which the carbonylated residues found in vivo are marked with asterisks. B, Immunoblot of purified Lb after 6 h of MCO at different FeCl3 and ascorbate (ASC) concentrations. CT, Control omitting ASC and FeCl3; Ox1, 2.5 mm ASC, 10 μm FeCl3; Ox2, 12.5 mm ASC, 50 μm FeCl3; Ox3, 25 mm ASC, 100 μm FeCl3; Ox4, 50 mm ASC, 200 μm FeCl3; Ox5, 75 mm ASC, 300 μm FeCl3. C, Immunoblot of purified Lb after 6 h of MCO at different FeCl3, ASC, and H2O2 concentrations. Ox5, 75 mm ASC, 300 μm FeCl3; Ox6, 75 mm ASC, 300 μm FeCl3, 1 mm H2O2; Ox7, 75 mm ASC, 300 μm FeCl3, 5 mm H2O2. Gels were loaded with 10 μg of protein per lane. D, Immunoblot of bean nodule extracts. Gels were loaded with 50 μg of protein per lane. For B to D, the apparent molecular masses (kD) of the monomer (M), dimer (D), and tetramer (T) are indicated. The anti-Lb antibody and the secondary antibody were used at dilutions of 1:1,000 and 1:40,000, respectively. Blots are representative of at least three independent experiments.