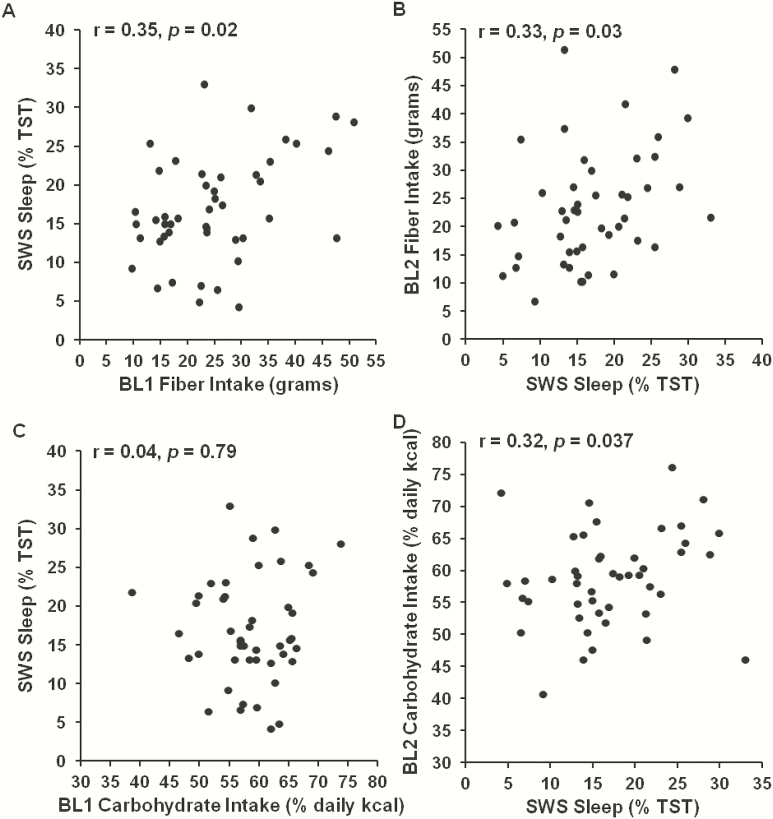
Figure 3—
Relationship between caloric intake variables and slow-wave sleep (SWS). Greater fiber intake during the day preceding (A) and the day following (B) the baseline sleep measurement was significantly associated with more SWS. Greater carbohydrate intake during the day following (D), but not the day preceding (C) the baseline sleep measurement was significantly associated with more SWS.