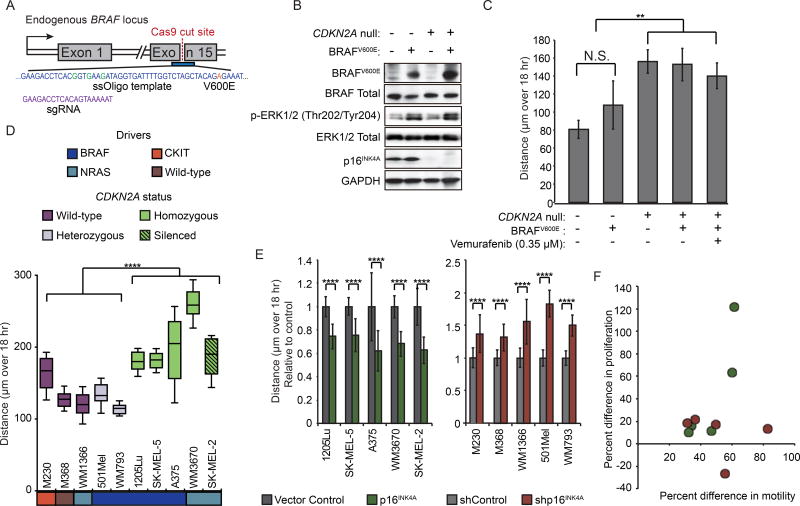
Figure 3. p16INK4A regulates motility independent of driver mutation.
(A) Strategy for introducing BRAFV600E point mutation. Center of HDR template is shown (blue) with point mutations causing intended codon change (orange) or silent mutations disrupting sgRNA binding (green) highlighted. sgRNA sequence shown in purple.
(B) Western blot detection of BRAFV600E and p16INK4A expression and ERK phosphorylation in engineered NHMs.
(C) Population motility analysis of NHMs engineered with BRAFV600E and/or CDKN2A deletion. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean of three experiments.
(D) Comparison of motility in ten melanoma lines with different genetic backgrounds. Lines were classified by activating driver mutation (BRAF, NRAS, CKIT or Wild-type) and CDKN2A status. CDKN2A status was designated as either wildtype and expressed (Wild-type), mono-allelic disruption and expressed (Heterozygous), bi-allelic disruption (Homozygous), or wild-type and silenced (Silenced). Box and whisker plot represents mean, 10th, 25th, 75th and 90th percentiles of forty cells per line.
(E) Effect of EF1a-driven p16INK4A expression on motility in CDKN2A null or silenced melanoma lines (left). Effect of shRNA-mediated p16INK4A knockdown on motility in p16INK4A expressing melanoma lines (right). Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean of forty cells per condition.
(F) Comparison of the effect of p16INK4A loss on proliferation and motility in ten melanoma lines. Red dots represent comparison of shRNA-mediated p16INK4A knock-down normalized to vector controls in p16INK4A expressing melanoma lines. Green dots represent comparison of vector controls normalized to EF1a-driven p16INK4A expression in CDKN2A null or silenced lines. No significant correlation between proliferation and motility was observed.
Asterisks indicate p value of ** <0.005 to **** <0.00005 from unpaired t-test. N.S. indicates no significant difference.
See also Figure S3.