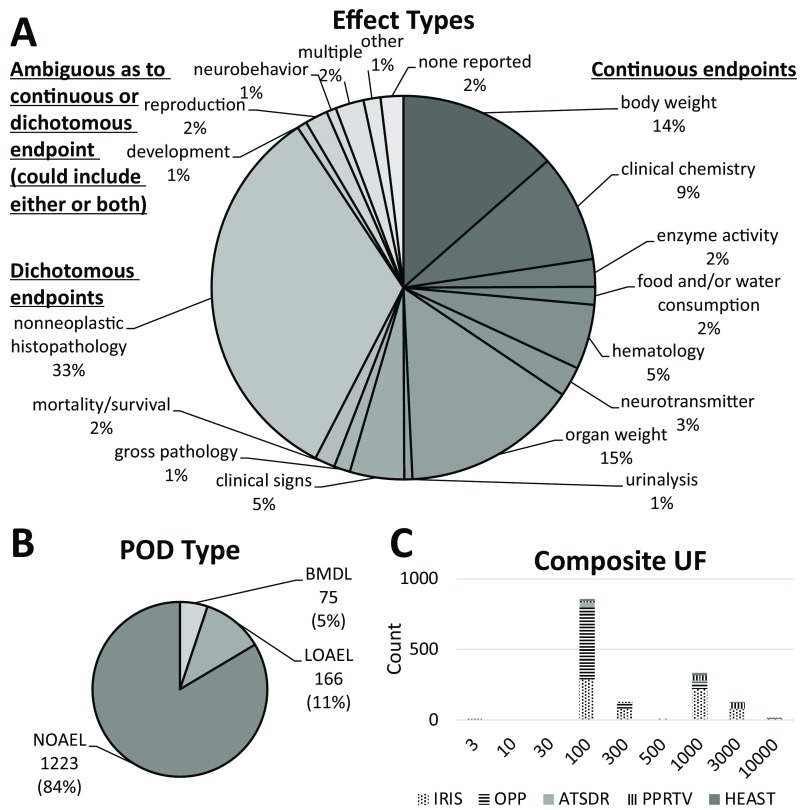
Figure 5.
Characteristics of the database of references doses (RfDs). (A) Distribution of toxicological effects, including continuous endpoints, dichotomous endpoints, and endpoints that could be either continuous or dichotomous. (B) Distribution of types of points of departure (POD), including NOAEL (no observed adverse effect level), LOAEL (lowest observed adverse effect level), and BMDL (benchmark dose lower confidence limit). (C) Distribution of composite uncertainty factors (UFs) applied across RfDs, depending on source (IRIS, Integrated Risk Information System; OPP, Office of Pesticide Programs; ATSDR, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry; PPRTV, Provisional Peer-reviewed Toxic Values; HEAST, Health Effects Assessment Summary Tables).