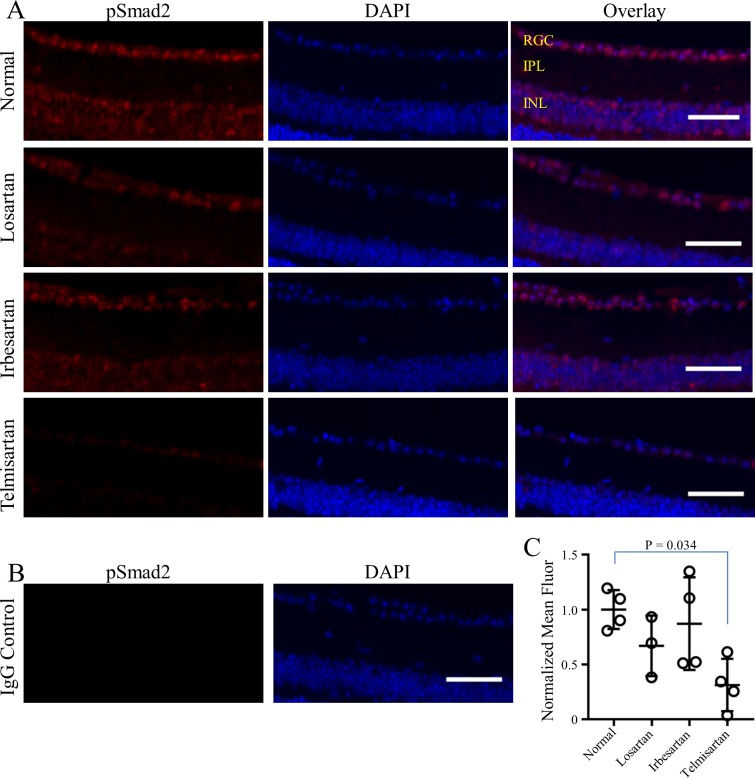
Fig 5. Reduced TGFβ signal transduction in the RGC layer of ARB-treated mice.
(A) Representative immunostaining for pSmad2 (red, left column) and DAPI-staining of cell nuclei (blue, middle column) shows nuclear pSmad2 in overlay images (pink, right column). Pattern indicates constitutive TGFβ signal transduction in the inner nuclear and RGC layers of mice fed normal chow (upper row) that is reduced in mice fed ARB-containing chows (lower three rows), most strongly by telmisartan (lower row). IgG negative control (B) shows lack of non-specific staining. Quantification of pSmad2 fluorescence (red) in the RGC layer (C) shows statistically significant reduction in telmisartan-treated mice, with a 70% reduction compared to normal fed mice (p = 0.034). Results are from duplicate experiments from one eye of each individual mouse; n = 4 for normal, irbesartan and telmisartan; n = 3 for losartan. Symbols represent the average pSmad2 red fluorescence for each mouse with mean/SD for each treatment shown in (C). Retinal layers are indicated (upper right panel, A): RGC = RGC layer; IPL = inner plexiform layer; INL = inner nuclear layer. Scale bars = 50 μm.