Figure 5.
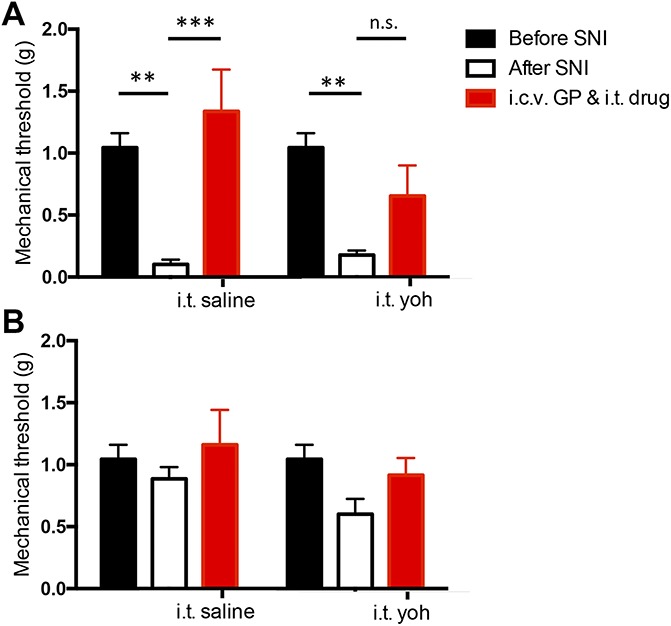
Blocking spinal α2 receptors reduces the antinociceptive effect of supraspinal gabapentin (GP). (A) After SNI, the mechanical withdrawal threshold of the injured paw differs significantly from its preinjury baseline level (**P < 0.01). Supraspinal GP (50 μg i.c.v.) increased the withdrawal threshold, demonstrating its antinociceptive effect. Intrathecal saline (n = 8) had no effect on the antinociceptive action of supraspinal GP (open black bars compared with filled red bars, ****P < 0.0001); i.t. yohimbine (5 μg, n = 8) reduced the antinociceptive effect of GP (open black bars compared with filled red bars, n.s., 2-way RM-ANOVA, the Sidak multiple comparison test; df = 14). (B) Supraspinal GP and i.t. yohimbine did not alter mechanical thresholds of the contralateral, uninjured paw. Data are mean ± SEM. ANOVA, analysis of variance; i.c.v., intracerebroventricular; i.t., intrathecal; n.s., not significant; RM-ANOVA, repeated-measures analysis of variance; SNI, spared nerve injury.
