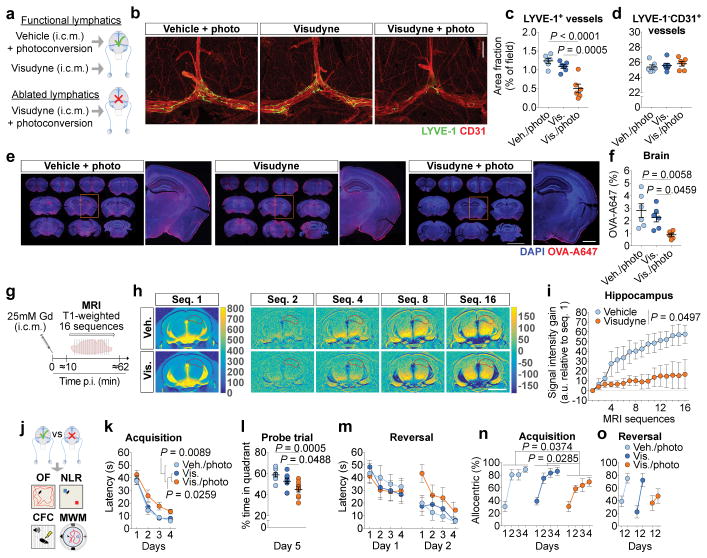
Figure 1. Impairing meningeal lymphatics affects brain CSF influx and ISF diffusion and worsens cognitive function.
a, Seven days after lymphatic ablation mice were injected with 5 μL of ovalbumin-Alexa647 (OVA-A647) into the cisterna magna (i.c.m.). b, Representative images of meningeal whole-mounts stained for LYVE-1/CD31 (scale bar, 1 mm). c, d, Quantification of area fraction (%) occupied by (c) LYVE-1+ lymphatic vessels and (d) LYVE-1−CD31+ blood vessels. e, Representative brain sections showing 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) and OVA-A647 (scale bar, 5 mm; inset scale bar, 1 mm). f, Quantification of OVA-A647 area fraction. Data in c, d and f is presented as mean ± s.e.m., n = 6 per group; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test was used in c, d and f; a–f is representative of 2 independent experiments; significant differences between vehicle/photoconversion and Visudyne/photoconversion were replicated in 5 independent experiments. g, Gadolinium (Gd) was injected (i.c.m.) and T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) acquisition was performed 7 days after meningeal lymphatic ablation. h, Representative images of sequence 1 and of Gd intensity gain in subsequent sequences (hippocampus delineated in red; scale bar, 3 mm). i, Quantification of the Gd signal intensity gain over 16 sequences (relative to sequence 1) in hippocampus. Data in i is presented as mean ± s.e.m., n = 4 per group; repeated measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test; g–i is representative of 2 independent experiments. j, Meningeal lymphatic ablation was performed twice and two weeks after the last intervention, open field (OF), novel location recognition (NLR), contextual fear conditioning (CFC) and Morris water maze (MWM) behavioral tests were performed (Extended data Fig. 5 for OF, NLR and CFC). k, Latency to platform (acquisition). l, Time spent (%) in the target quadrant (probe). m, Latency to platform (reversal). n, o, Allocentric navigation strategies (%) used in the MWM (n) acquisition and (o) reversal. Data in k–m and n, o are presented as mean ± s.e.m., n = 9 per group; repeated measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test was used in k, m, n and o; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test was used in l; significant differences between vehicle/photoconversion and Visudyne/photoconversion were replicated in 3 independent experiments.