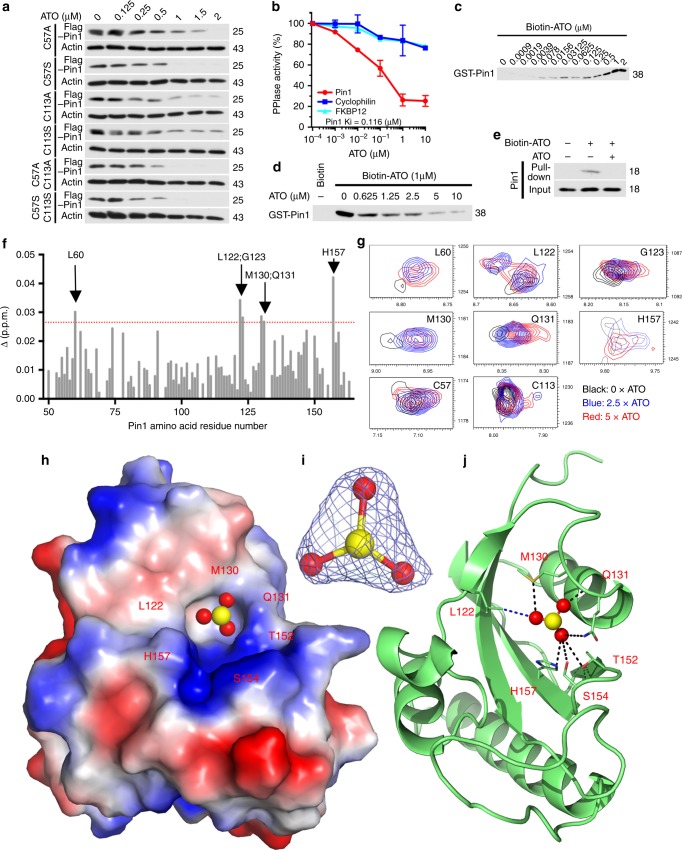
Fig. 2.
ATO directly binds to specific residues in the Pin1 active site via a previously unknown mechanism. a Cys residues in Pin1 are not required for ATO to degrade Pin1. Pin1 KO cells stably expressing Cys single or double Pin1 Ala or Ser mutants were treated with different concentrations of ATO, followed by Pin1 immunoblot. b ATO inhibits PPIase activity of Pin1, but not Cyp18 or FKBP12. Pin1, Cyp18, or FKBP12 was incubated with different concentrations of ATO, followed by chymotrypsin-coupled PPIase assay. c Biotin-ATO binds to Pin1. Pin1 was incubated with biotin-ATO, followed by isolating biotin-ATO-bound Pin1 for immunoblot (top) and plotting against ATO concentrations (bottom). d ATO binding to recombinant Pin1 can be competed by ATO. Biotin-ATO was incubated with recombinant Pin1, followed by incubation with ATO before subjecting biotin-ATO pulldown assay and Pin1 immunoblot. e ATO binding to cellular Pin1 can be competed by ATO. The 231 cells were treated with or without ATO and then subjected to biotin-ATO pulldown assay, followed by Pin1 immunoblot, along with Pin1 imputs. f, g NMR analysis of ATO-Pin1 binding. Weighted average chemical shift difference Δ of 15N-Pin1 upon addition of 5× ATO was calculated as |ΔH| + (1/5)|ΔN| in p.p.m. and plotted as a function of residue number (f). Upon addition of 2.5× or 5× ATO to Pin1, total six residues in Pin1 show significant chemical shift changes at both ATO concentrations, with two Cys that show no obvious chemical shift changes being highlighted (g). h–j The co-crystal structure of the Pin1-ATO complex. ATO was mixed and co-crystallized with 500 µM Pin1, followed by collecting diffraction data at synchrotron beamline 24ID using and integrating and scaling data sets using XDS. Identical novel trigonal electron density in shape was noted at the Pin1 active site in multiple co-crystals (h, i). The apexes of this electron density are positioned within hydrogen bonding distances (dark green) of side chains from Met130, Gln131, Thr152, Ser154, and His157 and within van der Waals distance (blue) of side chain from Leu122 in the Pin1 active site (j)