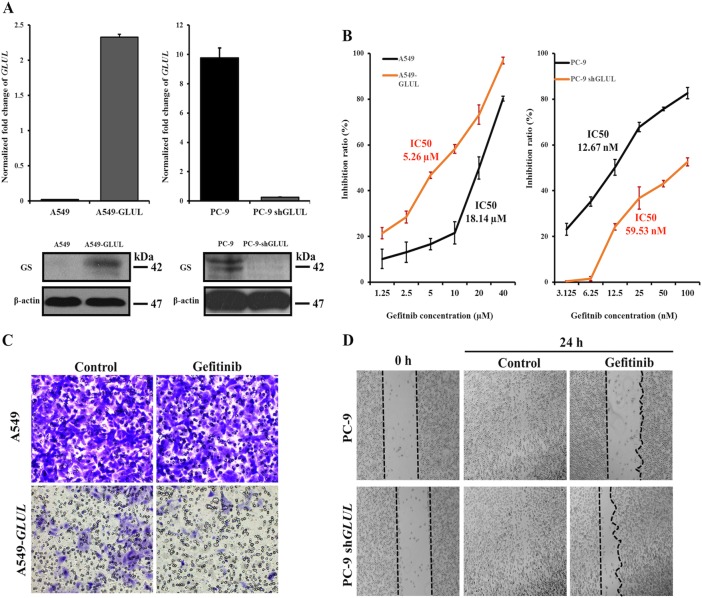
Fig. 5. Expression of GLUL in A549 cells sensitizes them to the gefitinib treatment and decreases cell motility, whereas the loss of GLUL expression in PC-9 cells increases resistance to gefitinib treatment and increases cell motility.
a qRT-PCR and western blotting were used to assess the GLUL mRNA level and the GS protein level, respectively, to identify the GLUL knock-in efficacy in A549 cells and the GLUL knockout efficacy in PC-9 cells. The bars shown are normalized to the GAPDH control and represent the mean ± SD of triplicate samples. b MTT assays detected the cell growth inhibition ratios following the gefitinib treatment in GLUL-expressing A549 cells and GLUL knockout PC-9 cells. c Based on the transwell assay, significantly fewer A549-GLUL cells invaded the membrane than A549 cells, and the 24-h gefitinib treatment further suppressed the invasion of A549-GLUL cells. In contrast to A549-GLUL cells, the gefitinib treatment did not inhibit the invasion of A549 cells. d Scratch wound-healing assays showed that the knockout of GLUL in PC-9 cells resulted in a decrease of the ability of cells to close a wound after the 24-h treatment with gefitinib