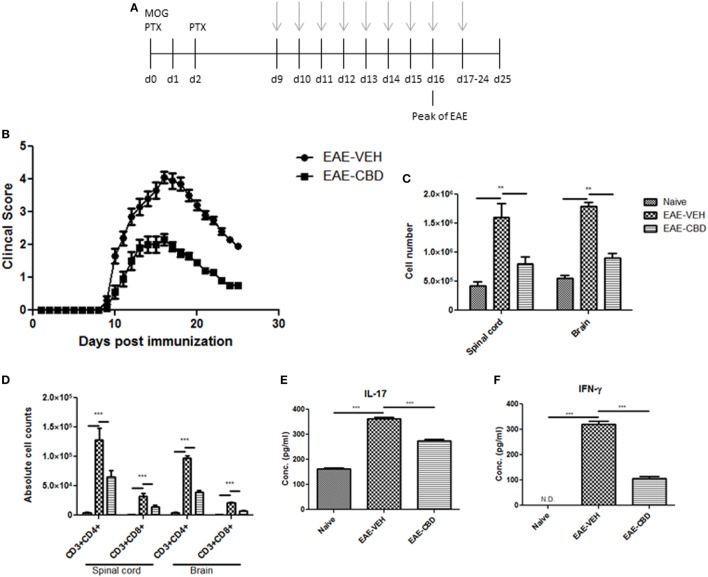
Figure 1.
Effect of cannabidiol (CBD) treatment on the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in C57BL/6 mice. (A) Time line schematic of studies. CBD treatment was administered at time points with gray arrows. Data were assessed at peak of disease unless otherwise stated. (B) Clinical scores (n = 10 mice per group); data were presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed for significance using Mann–Whitney U test. Comparisons were considered significant at p ≤ 0.05, denoted as *. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments; in each experiment, disease incidence was 100% for each group. (C) Total mononuclear cell infiltrates in central nervous system. (D) Absolute cell counts for CD3+CD4+ T cells and CD3+CD8+ T cells; mononuclear cells stained with corresponding Abs and then enumerated using total cell count and frequency from flow cytometry. (E) Serum expression level of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-17 and IFNγ analyzed by ELISA. In panels (D–F), all data represented as mean ± SEM. ANOVA, ***p < 0.0001, and **p < 0.001 with Tukey’s post hoc test.