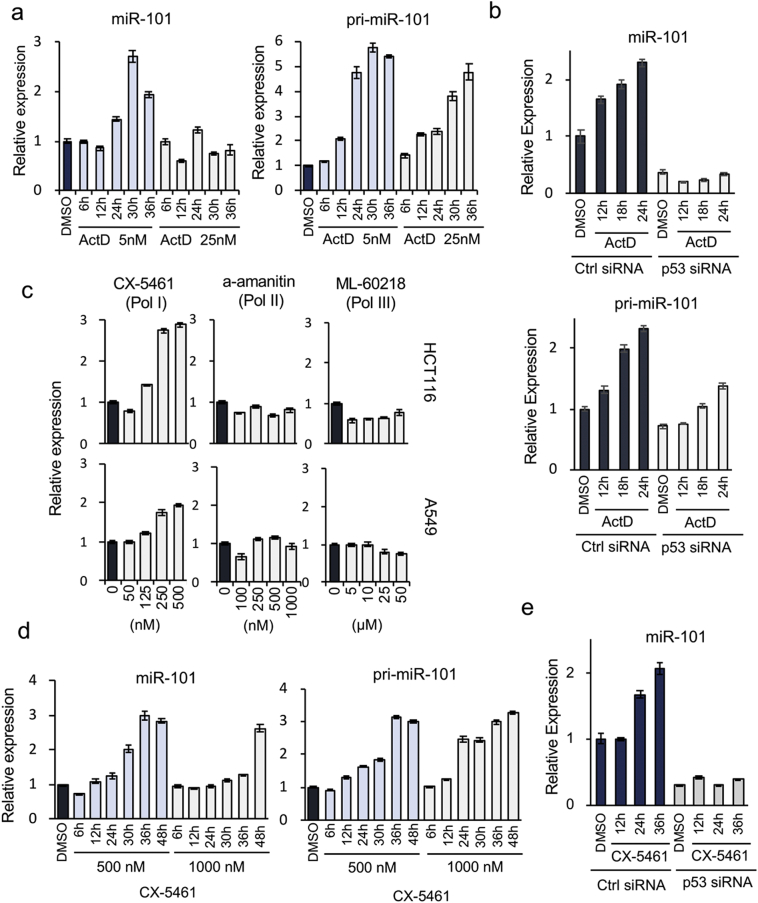
Fig. 5.
Activation of miR-101 expression by inhibition of RNA polymerase I. (a) Left and right graphs show time courses of expression of miR-101 and pri-miR-101, respectively, in HCT116 cells following treatment with the indicated concentrations of ActD. Data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate reactions after normalization against the corresponding level of TBP mRNA, and are representative of at least two independent experiments. Incubation times are provided below the graphs. (b) miR-101 and pri-miR-101 expression, as determined by qRT-PCR, after treatment with 5 nM ActD in the presence or absence of p53. Data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate reactions after normalization against the corresponding level of PPIA mRNA, and are representative of two independent experiments. (c) miR-101 activation by the indicated concentrations of specific RNA polymerase inhibitors. Upper and lower graphs depict results for HCT116 and A549, respectively. CX-5461, alpha-amanitin, and ML-60218 are inhibitors of Pol I, Pol II, and Pol III, respectively. Concentrations of inhibitors used for the assay are listed below the lower graphs. Data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate reactions after normalization against the corresponding level of TBP mRNA, and are representative of at least two independent experiments. (d) miR-101 and pri-miR-101 expression in HCT116 cells after treatment with two concentrations of CX-5461 were measured at the time points indicated below the graph. Data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate reactions after normalization against the corresponding level of TBP mRNA, and are representative of at least two independent experiments. (e) Expression of miR-101 after exposure of HCT116 cells to CX-5461 in the p53 KD cells. Data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate reactions after normalization against the corresponding level of PPIA mRNA, and are representative of two independent experiments.