Fig. 2.
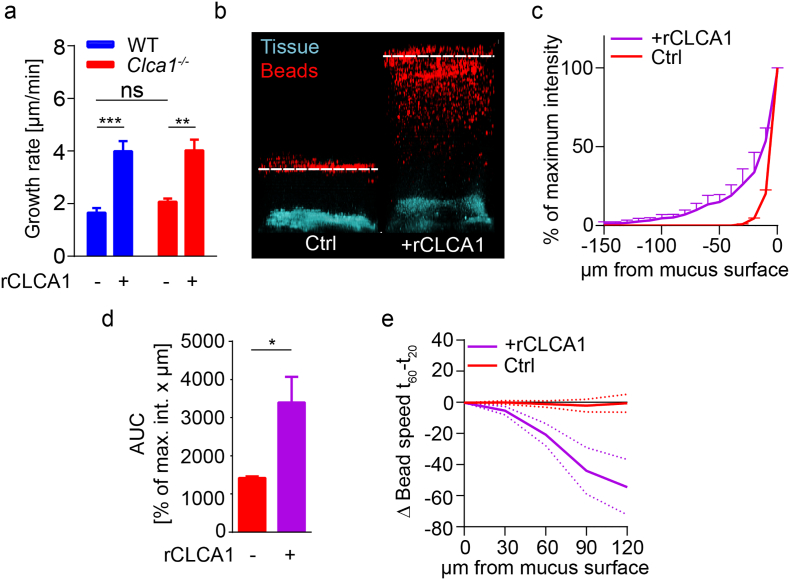
CLCA1 causes increased mucus growth and penetrability in WT and Clca1−/− mice. (a) Distal colon mucus growth rate measured in WT and Clca1−/− mice without (−) and with (+) 5 μg rCLCA1 applied apically (n = 4–7). (b) Representative z-stack projections of bacteria sized bead (1 μm, red) distribution in distal colon mucus of WT and Clca1−/− at 30 min after control (PBS) treatment (left panel), or after rCLCA1 (10 μg) treatment (right panel) (n = 8). Dashed line indicates mucus surface. (c) Distribution of beads in control or rCLCA1 (10 μg) treated Clca1−/− mucus. The z-position with highest bead intensity was defined as the mucus surface, and the bead penetrance in the mucus was plotted as % of maximum intensity at each z-position below the mucus surface (n = 4). (d) Area under curve (AUC) analysis of bead penetrability data (c) comparing rCLCA1 treated with control mucus (n = 4). (e) Change in average bead speed in different z-planes above the mucus surface between t = 20 min and t = 60 min in control or rCLCA1 (10 μg) treated Clca1−/− mucus, where the treatments were applied at t = 30 min. Bead mobility data is shown in Video S1, Video S2 (n = 3–5). Data is presented as mean ± SEM; * p ≤ .05, ** p ≤ .01, *** p ≤ .001 with either two-way ANOVA with Tukey's MCT (a) or unpaired 2-tailed t-test (d). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
CLCA1 causes increased mucus growth and penetrability in WT and Clca1−/− mice. (a) Distal colon mucus growth rate measured in WT and Clca1−/− mice without (−) and with (+) 5 μg rCLCA1 applied apically (n = 4–7). (b) Representative z-stack projections of bacteria sized bead (1 μm, red) distribution in distal colon mucus of WT and Clca1−/− at 30 min after control (PBS) treatment (left panel), or after rCLCA1 (10 μg) treatment (right panel) (n = 8). Dashed line indicates mucus surface. (c) Distribution of beads in control or rCLCA1 (10 μg) treated Clca1−/− mucus. The z-position with highest bead intensity was defined as the mucus surface, and the bead penetrance in the mucus was plotted as % of maximum intensity at each z-position below the mucus surface (n = 4). (d) Area under curve (AUC) analysis of bead penetrability data (c) comparing rCLCA1 treated with control mucus (n = 4). (e) Change in average bead speed in different z-planes above the mucus surface between t = 20 min and t = 60 min in control or rCLCA1 (10 μg) treated Clca1−/− mucus, where the treatments were applied at t = 30 min. Bead mobility data is shown in Videos S1 and S2 (n = 3–5). Data is presented as mean ± SEM; * p ≤ .05, ** p ≤ .01, *** p ≤ .001 with either two-way ANOVA with Tukey's MCT (a) or unpaired 2-tailed t-test (d).