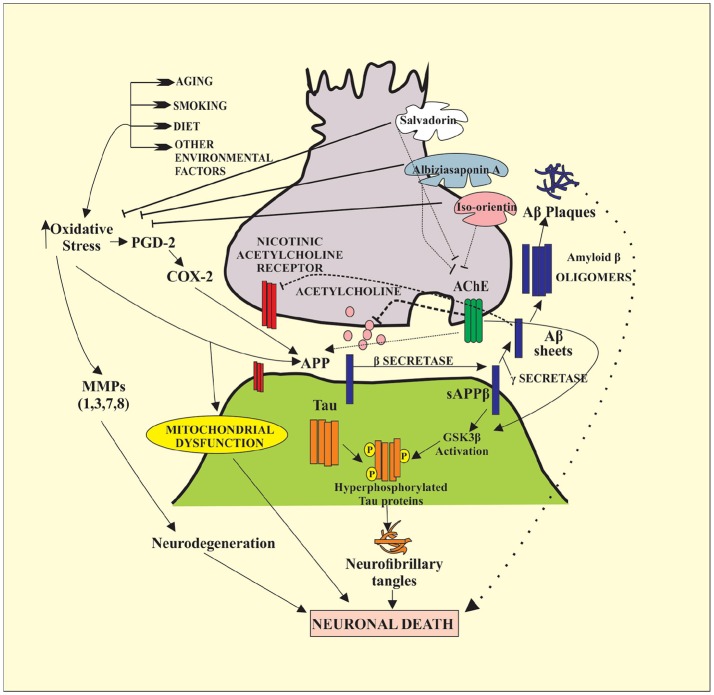
Figure 4.
The mechanism of Alzheimer's disease (AD). It shows the role of Acetylcholine Esterase (AchE) and oxidative stress in the neurodegeneration. Oxidative stress and AchE up-regulates the activity of Amyloid precursor proteins (APPs). Moreover, oxidative stress is involved in the activation of several MMPs and enzymes cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). MMPs are directly responsible for the degradation of extracellular membrane (ECM) that leads to neurodegeneration. Under the action of enzyme β-secretase APPs gets converted into serum APPβ that later with the action of γ-secretase is converted into amyloid-β sheets. These amyloid-β sheets ultimately form amyloid β plaques. Alzheimer disease is often characterized with the presence of amyloid β plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and hyperphosphorylated tau proteins. Tau proteins are hyperphosphorylated under the action of GSK3β which is activated by the activity of sAPPβ. Cumulatively, all of the discussed factors are involved in the neurodegeneration, which leads to the Alzheimer disease. Most of the drugs used in the following case are AchE inhibitors. They halt the AchE so, there will be enough neurotransmission present for the proper neuronal functioning. Likewise, in the current study, salvadorin, albiziasaponin and iso-orientin, significantly blocked the activity of AchE to cause neuroprotection.