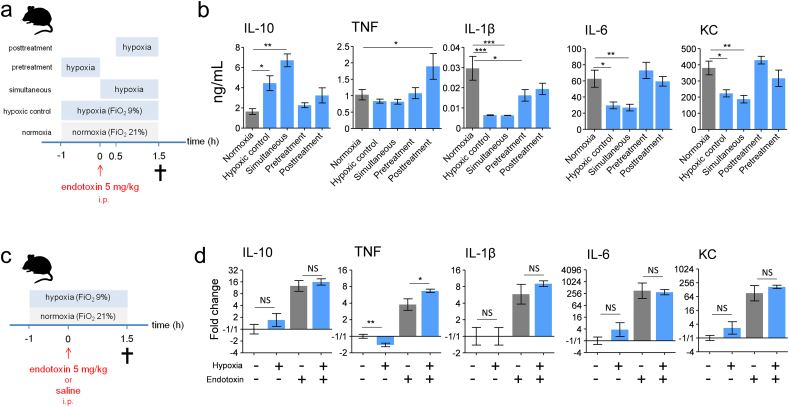
Fig. 2.
The anti-inflammatory effects of short-term hypoxia are rapidly constituted and post-transcriptionally regulated.
(a) Experimental setup. C57BL/6 mice were randomized to normoxia or one of the following hypoxia modalities: hypoxic control: hypoxia starting 1 h before endotoxin administration until 1.5 h thereafter; simultaneous: hypoxia starting simultaneous with endotoxin administration until 1.5 h thereafter; pretreatment: hypoxia only in the hour before endotoxin administration; posttreatment: hypoxia starting 0.5 h after endotoxin administration until 1.5 h thereafter. Endotoxin (5 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally (i.p). (b) Plasma concentration of IL-10, TNF, IL-1β, IL-6 and KC. (c) Experimental setup. C57BL/6 mice were randomized to short-term hypoxia or normoxia and intraperitoneally injected with endotoxin (5 mg/kg) or saline. (d) mRNA expression of IL-10, TNF, IL-1β, IL-6 and KC measured in splenic tissue. n = 8 per group in all experiments. Data expressed as mean (± s.e.m.) or mean (± s.e.m.) fold change related to normoxic-saline condition on a 2log scale. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 (compared to normoxia calculated using one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett's test for panel b; unpaired Student's t-test for panel d).