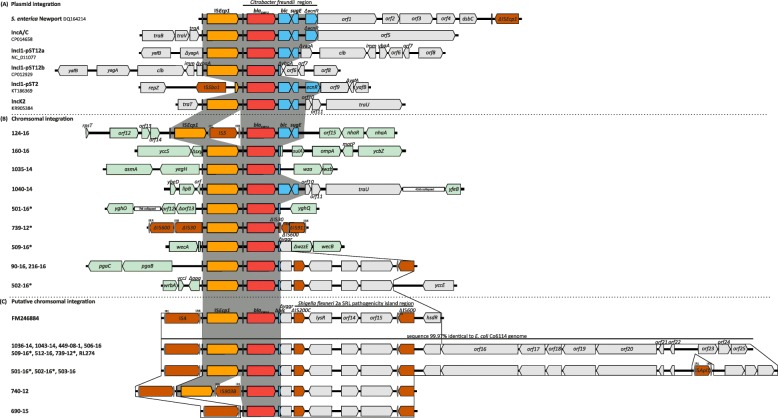
Fig. 2.
Surrounding genetic regions of blaCMY-2 in the 164 E. coli isolates from the different reservoirs. ISEcp1 and the adjacent from Citrobacter freundii mobilized conserved chromosomal region containing blaCMY-2, blc, sugE and ecnR is highlighted in dark grey across the different backgrounds. The color code is as follows: ISEcp1 is in orange, blaCMY-2 in red, blc, sugE, and ecnR are in blue, insertion sequence elements (IS) in brown, E. coli chromosomal genes adjacent the blaCMY-2 complex integration are in light green. The black rectangles represent the inverted repeats of ISEcp1; further inverted repeats are highlighted by grey rectangles. a Genetic surrounding of blaCMY-2 found on different plasmid backbones (IncA/C (accession number: CP014658), IncK2 (accession number: KR905384), IncI1-pST2 (accession number: KT186369), IncI1-pST12a (accession number: NC_011077), IncI1-pST12b (accession number: CP012929)) compared to the genetic surrounding of blaCMY-2 in S. enterica serovar Newport (accession number: DQ164214). b Genetic surrounding of blaCMY-2 in eight E. coli isolates with chromosomally encoded blaCMY-2. Isolates with twofold encoded blaCMY-2 are indicated by an asterisk, the second copy was putatively chromosomally integrated. c Putative chromosomal integration of blaCMY-2 in 15 isolates compared to a previously published sequence (accession number FM246884). The presence of a Shigella flexneri 2a SRL pathogenicity island region downstream of truncated genes blc and yggr is shown. Isolates with two blaCMY-2 genes (additional putative chromosomal integration site) are indicated by an asterisk, respectively