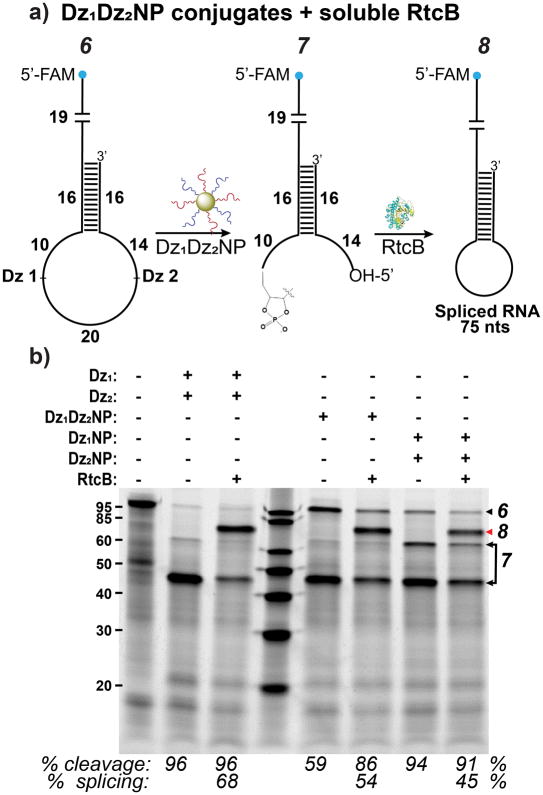
Figure 4.
DNAzyme conjugates (Dz1Dz2NPs) can splice with excess soluble RtcB. (a) Scheme showing splicing by Dz1Dz2NPs and RtcB on RNA substrate. (b) Splicing by soluble DNAzymes is compared to NPs with either both or single Dz’s attached. Red arrow indicates splice product. Reaction conditions: 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM Mn2+, 0.4 μM substrate 6, 0.4 mM GTP, 2.2 μM RtcB, lanes 2–3, 0.4 μM Dz(s), lanes 5–6, 9 nM Dz1Dz2NPs, lanes 7–8, 9 nM Dz1NP and Dz2NP. Cleavage was conducted at 37°C for 2 hrs and splicing at 37°C for 1 hr. Note that the cleavage yield increased in lane 6 compared to lane 5 likely due to the additional 1 hr incubation time following treatment with RtcB.