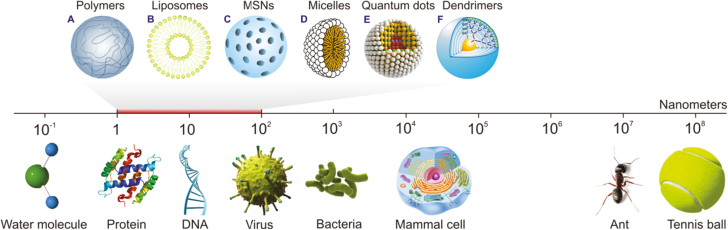
FIGURE 2.
Illustration comparing the sizes of various particles and the main units of living entities. A, Polymeric nanoparticles are solid polymeric matrices. B, Liposomes are vesicles formed from a phospholipid bilayer that mimics the cell membrane structure. C, Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) comprise a solid framework with a porous structure and large surface area; different functional groups may be attached at the surface to target the drug moiety to a particular site. D, Micelles comprise an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant molecules dispersed in a liquid colloid. A typical micelle in aqueous solution forms an aggregate with the hydrophilic “head” regions in contact with the surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydrophobic single-tail regions in the center of the micelle. E, Quantum dots are semiconductor particles that are so small (several nanometers) that their optical and electronic properties differ from those of larger particles. F, Dendrimers are highly branched, star-shaped macromolecules with nanometer-scale dimensions. They are defined by 3 components: a central core, an interior dendritic structure (the branches), and an exterior surface with functional surface groups.