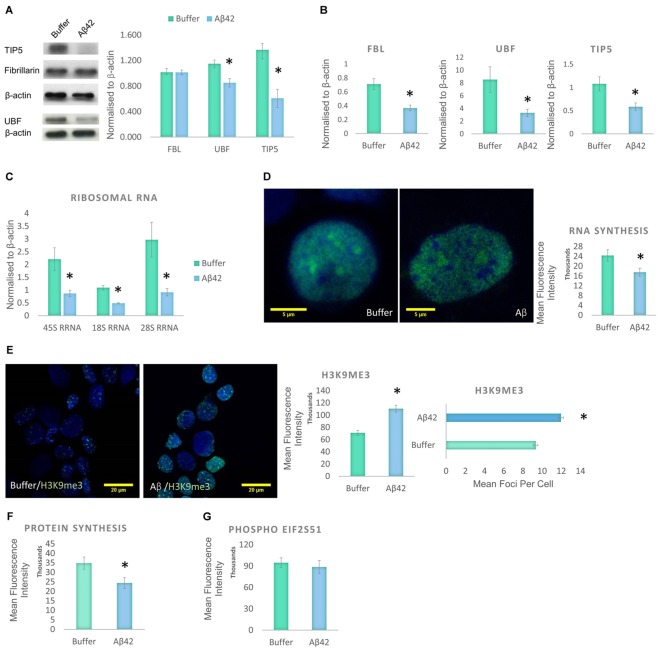
FIGURE 4.
Aβ42 induces nucleolar stress and inhibit RNA and Protein Synthesis 24 h post-incubation. (A) Western blotting revealed that Aβ treatment led to a significant decrease in UBF, TIP5, but not FBL. Normalized to β-actin. (B) qPCR analysis showed a significant reduction of UBF, TIP5, and FBL transcripts. Normalized to β-actin or TBP. (C) qPCR analysis of rDNA transcription and processing showed that the Aβ incubation resulted in a significant decrease in 45S pre-rRNA synthesis and processing of 18S rRNA and 28S rRNA. Normalized to β-actin or TBP. (D) Quantitative Click-iT RNA immunofluorescence labeling showed that the Aβ causes a global reduction in newly synthesized RNA, (E) which is associated with a nuclear increase in H3K9me3 intensity and foci. (F) Quantitative Click-iT HPG Alexa Fluor 488 immunofluorescence labeling showed a significant decrease in nascent protein synthesis following the Aβ treatment. (G) Quantitative immunofluorescence labeling for phosphor S51 eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A (EIF2A-P) showed no changes following the Aβ treatment. For A, N = 5, B–E, N = 4 and F,G, N = 3, ∗P < 0.05 (See also Supplementary Figure 1).