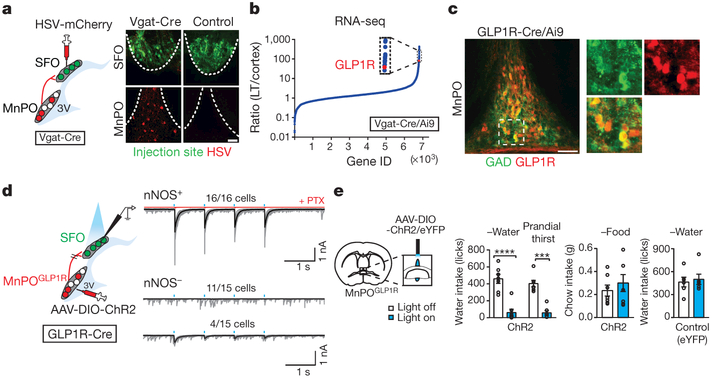
Figure 2 |. GLP1R-expressing GABAergic neurons in the MnPO are a major source of inhibitory input to the SFO.
a, GABAergic input to the SFO. Representative image of the SFO and MnPO after co-injection of AAV-Syn-GCaMP6s (green) and HSV-mCherry (red) in the SFO (one out of four mice). b, GLP1R expression is enriched in inhibitory neurons from the lamina terminalis (LT) relative to the cortex. c, MnPOGLP1R neurons are GABAergic (84.7 ± 3.4% of GAD+ neurons are tdTomato+, n = 3 mice, representative images are from one out of three mice). These neurons did not overlap with glutamatergic neurons (4.3 ± 0.9% overlap, n = 3 mice, Extended Data Fig. 6a). d, The MnPOGLP1R → SFO monosynaptic connection. MnPOGLP1R neurons send monosynaptic inhibitory input to SFOnNOS neurons. e, Optogenetic stimulation of MnPOGLP1R neurons selectively suppresses water intake (n = 7 mice for ChR2 and n = 6 mice for control). ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, by paired two-tailed t-test. All error bars show mean ± s.e.m. Scale bars, 50 μm.