Figure 1.
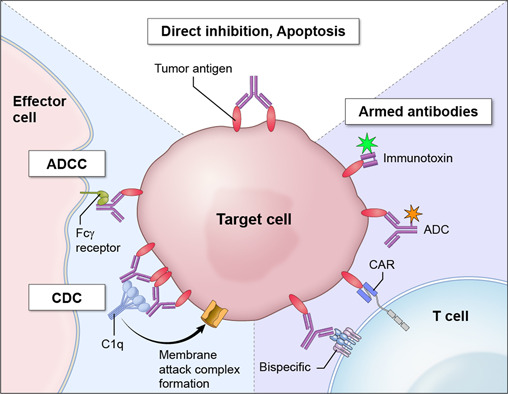
Mechanisms of antibody-based cancer therapies. Antibodies to cell surface antigens are potentially effective in several ways. First, antibodies directly inhibit tumor cell proliferation via inducing apoptosis or inhibiting key signaling pathways for cell growth. Second, antibodies can kill targeted tumor cells by initiating antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Third, antibodies can recruit immune cells such as T cells or chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. Finally, antibodies can be used to deliver cytotoxins including bacterial toxins (immunotoxins) or small toxic molecules (antibody drug conjugates) to kill tumor cells.
