Figure 2.
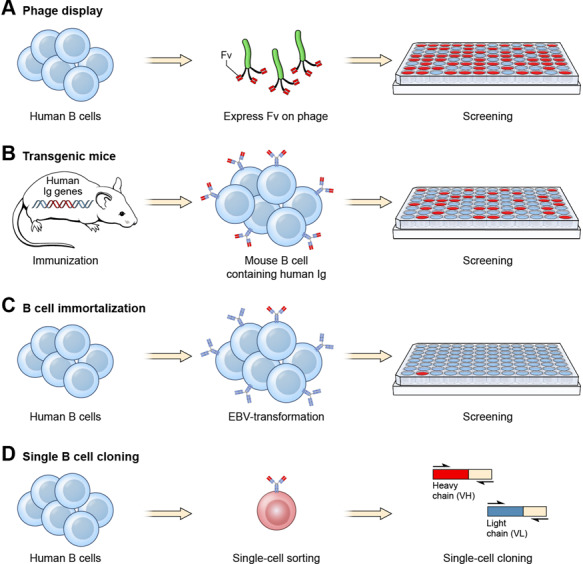
Examples of how human mAbs specific for tumor antigens can be isolated. Four major approaches have been developed to isolate human mAbs. (a) Phage display. A large phage display library is commonly used to isolate human scFv or Fab specific for an antigen [11]. After 3–5 rounds of panning, tumor-specific phage clones may be enriched and identified commonly by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). More recently, human single-domain antibodies are also isolated by phage display [28,29]. (b) Transgenic mice. Mice producing human Ig genes are immunized with a tumor antigen. Mouse hybridomas are created to produce stable mouse B cell lines. Mouse B cells expressing tumor-specific human mAbs are screened in ELISA using culture supernatant. (c) B cell immortalization. Human B cells are immortalized by EBV transformation. A large number of immortalized B cell clones are screened for antigen binding. (d) Single B cell sorting. Memory B cells are sorted by flow cytometry for the isolation of rare single B cells (<1%) for antigen binding followed by single-cell cloning by RT-PCR.
