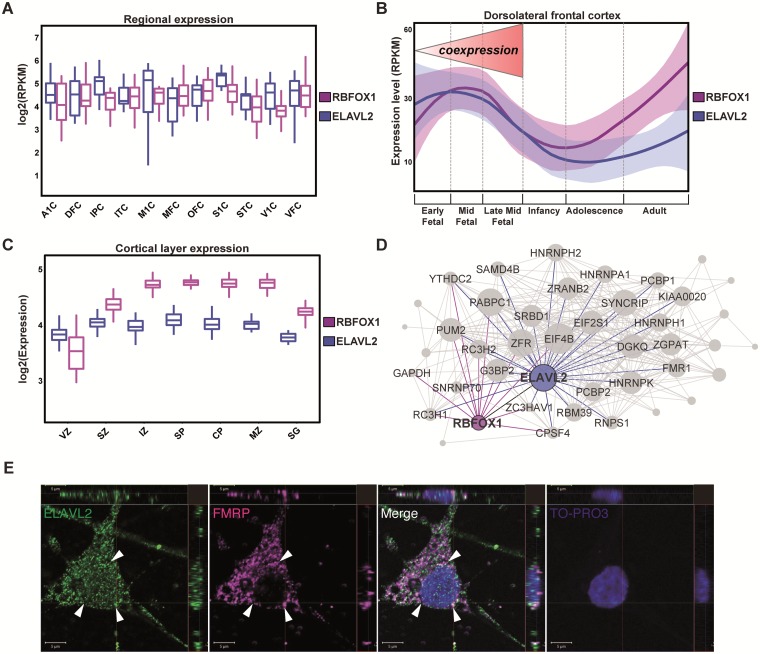
Figure 1.
ELAVL2 expression in human brain and phNs. (A) Expression distribution of RBFOX1 and ELAVL2 in fetal cortical regions (A1C, primary auditory cortex; DFC, dorsolateral frontal cortex; IPC, inferior parietal cortex; ITC, inferior temporal cortex; M1C, primary motor cortex; MFC, medial frontal cortex; OFC, orbital frontal cortex; S1C, primary sensory cortex; STC, superior temporal cortex; V1C, primary visual cortex; VFC, ventral frontal cortex). (B)ELAVL2 and RBFOX1 expression comparison in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex throughout the lifespan. The fetal developmental period in which RBFOX1 and ELAVL2 are strongly co-expressed is indicated. (C) Expression distribution of ELAVL2 and RBFOX1 in cortical layers (VZ, ventricular zone; SZ, subventricular zone; IZ, intermediate zone; SP, subplate; CP, cortical plate; MZ, marginal zone; SG, subpial granular layer). (D) Co-expression sub-module of RNAbps in prefrontal fetal cortex. Interactions represent potential protein interactions between RNAbps predicted by co-expressed genes. Each link corresponds to a weight calculated according to the correlation of the gene sets between nodes (see Methods section). RNAbps are preselected as nodes in the network. Shown are links between ELAVL2 (blue), RBFOX1 (purple), FMR1 (green) and other RNAbps (grey). (E) Co-localization confocal images of ELAVL2 and FMRP in phNs. Arrows indicate the perinuclear localization of both RNAbps. TO-PRO-3 is used to identify nuclei. Scale bar, 5 μm.