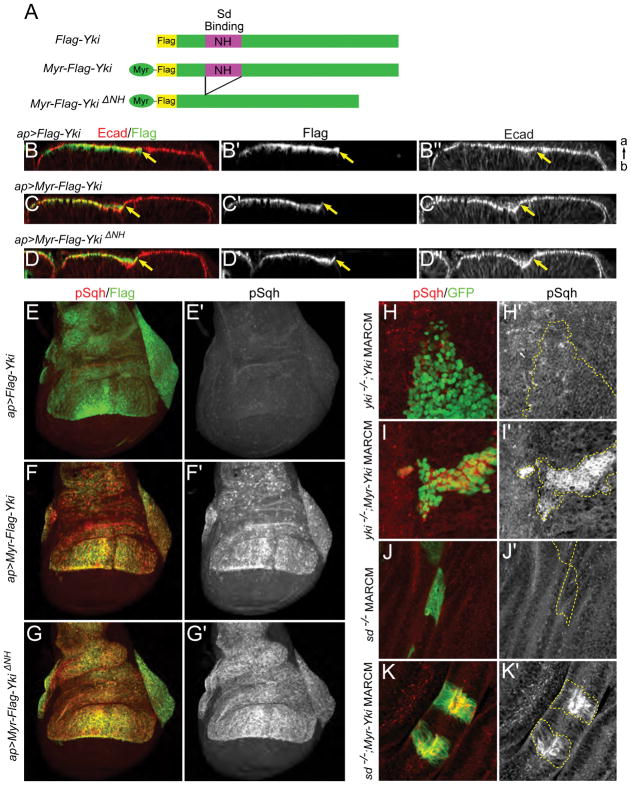
Figure 2. Cortical Yki promotes activation of myosin independently of Yki transcriptional activity.
(A) Cartoons showing UAS transgenes used in B–K. To provide a membrane tether, an N-terminal myristoylation signal sequence was added to Yki (Myr-Yki) or YkiΔNH (Myr-YkiΔNH). The NH domain binds Scalloped (Sd).
(B–D″) Ectopic expression of membrane-associated Yki induces indentation of the epithelium. apterous-Gal4 (ap-Gal4) was used to drive expression of transgenes in the dorsal compartment of wing discs. Optical cross-sections of the epithelium show that expression of Myr-Yki or Myr-YkiΔNH, but not wild-type Yki, induces indentation of wing disc epithelium at the expression boundary (marked by yellow arrows). Ecad staining marks adherens junctions. a, apical; b, basal.
(E–G′) Ectopic expression of membrane-associated Yki induces increased myosin activation. Anti-phospho-Sqh (pSqh), which specifically recognizes activated myosin regulatory light chain, was used to assay myosin activation. Expression of Myr-Yki or Myr-YkiΔNH, but not wild-type Yki, induces a dramatic increase in pSqh staining, indicating increased myosin activation. Images are maximal projections of apical optical sections.
(H–I′) Myosin activation caused by membrane-associated Yki is not dependent on endogenous Yki. Either wild-type Yki or Myr-Yki is expressed in yki null (ykiB5) mitotic clones (marked by GFP expression) using the MARCM technique. pSqh staining increases dramatically in Myr-Yki expressing cells but not in wild-type Yki expressing cells, suggesting that myosin activation is not downstream of Yki transcriptional activity.
(J–K′) Myosin activation caused by membrane-associated Yki is not dependent on Sd. When expressed in sd null (sd47M) mitotic clones (marked with GFP) using the MARCM technique, Myr-Yki induces increased pSqh, indicating that Yki/Sd-mediated transcription is not required for myosin activation.
See also Figure S1.