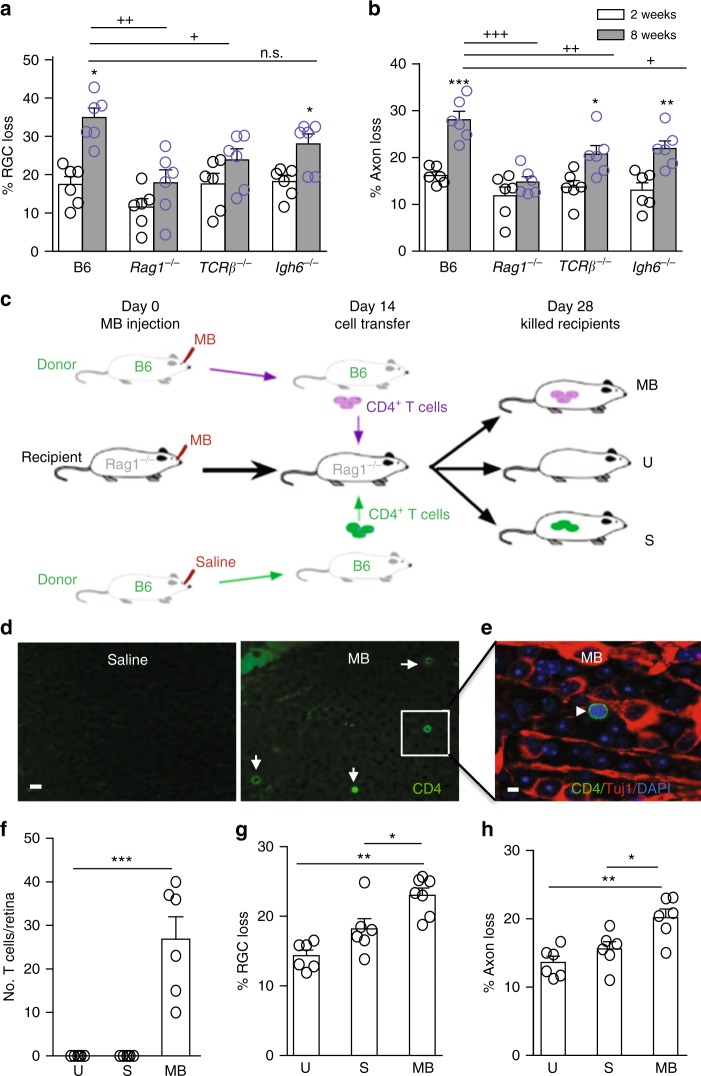
Fig. 2.
T cells are required for the prolonged retinal neurodegeneration. a, b Quantification of RGC (a) and axon (b) loss in B6, Rag1−/−, TCRβ−/−, and Igh6−/− mice at 2 (white box) and 8 (gray box) weeks after anterior chamber MB injection. n.s. nonsignificant, +P < 0.05, ++P < 0.01, +++P < 0.001 by ANOVA comparing between B6 and indicated mutant mice at 8 weeks post MB injection; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by ANOVA comparing between 2 and 8 weeks post MB injection of mice with the same genotype (n = 8/group). c Scheme of adoptive CD4+ T-cell transfer. Both donor B6 and recipient Rag1−/− (Rag1−/−) mice were injected with MB or saline into the anterior chamber. Fourteen days later, CD4+ T cells were isolated from the spleens of donor mice and injected via tail vein into Rag1−/− mice that had received MB injection 14 days earlier. d–h Fourteen days post cell transfer, T-cell infiltration and RGC and axon loss in Rag1−/− mice were analyzed. Retinal flat-mounts were stained with an anti-CD4 antibody (green), Tuj1 (red), and DAPI (blue). Shown are anti-CD4-stained (d) and overlay (e, from inset of d) images of retinal flat-mounts taken from Rag1−/− recipient mice receiving CD4+ T cells from saline- or MB-injected B6 mice. Arrows point to CD4+ cells. Scale bar: 25 µm (d) and 10 µm (e). Quantification of infiltrated T cells (f), and RGC (g) and axon (h) loss in glaucomatous Rag1−/− recipient mice that received no CD4+ T cells (U uninjected) or donor CD4+ T cells from saline-injected (S or normal IOP donor) and MB-injected (MB or glaucomatous donor) B6 mice 2 weeks post cell transfer. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 by ANOVA (n = 6/group)