Fig. 3.
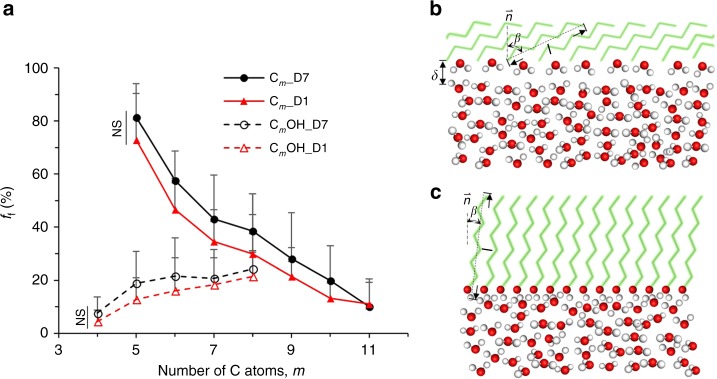
Deep-supercooled water sealed with linear alkanes and primary alcohols. a ff of 1 ml deep-supercooled (DSC) water at −20 °C. n = 7, N = 87. Error bars represent standard deviations. When m > 11 for linear alkanes and m > 8 for primary alcohols, the sealing agents are frozen at −20 °C and cause DSC water frozen. When m < 5, the linear alkanes are gaseous under atmospheric condition and not suitable for sealing. When m < 4, the primary alcohols are miscible with water and not suitable for sealing either. b, c Schematic configurations of alkane/water (b) and alcohol/water interface (c), respectively. The alkane and alcohol molecules are displayed without aliphatic hydrogen atoms and colored in light green. The O and H atoms in hydroxyl group of alcohol and water are shown in red and white dots, respectively