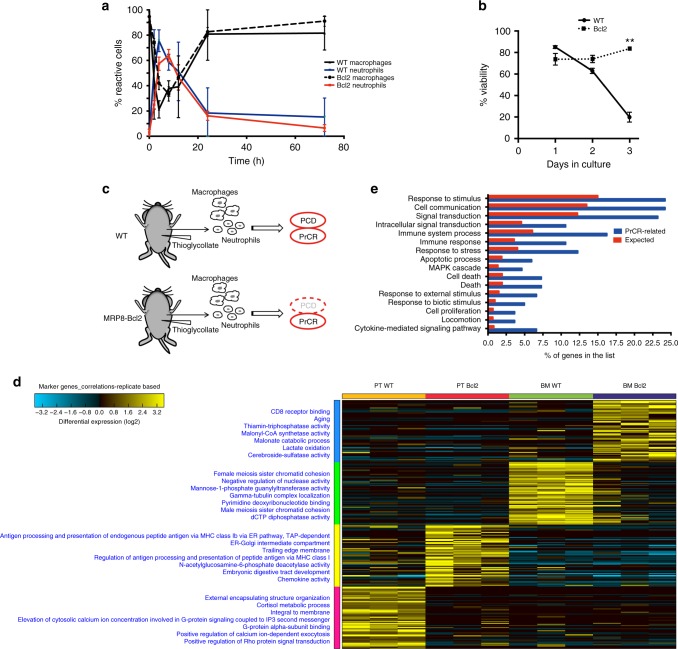
Fig. 1.
Viable aged neutrophils are cleared through activation of program cell removal. a Analysis of neutrophil and macrophage cell populations after thioglycollate injection to WT and MRP8-Bcl2 mice. Peritoneal cells were collected and analyzed at 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, and 72 h after thioglycollate injection. Similar lifespan was observed for WT and Bcl2 macrophages and neutrophils. Macs, macrophage;s WT, wild-type; PMN, neutrophil/polymorphonuclear cell. Results are representatives of three independent experiments. n = 3 mice for each time point. Error bars represent standard deviation. Cells were identified by surface markers such as CD11b+F4/80-GR1++ (Neutrophils), CD11b+F4/80+ (macrophages). Percentage reactive cells, the % of the total viable cells found in the peritoneum after induction of peritonitis. b WT but not Bcl2 neutrophils undergo cell death. WT and Bcl2 neutrophils were collected and cultured in vitro for 72 h. Cell viability was examined by AnnexinV and DAPI staining. Cells that were AnnexinV-DAPI- were considered as viable cells. n = 3. **P < 0.01 (t-test) for viability between WT and Bcl2 neutrophils. Error bars represent standard deviation. c A schematic showing peritonitis in WT and MRP8-Bcl2 mice. WT neutrophils undergo both programmed cell death (PCD) and programmed cell removal (PrCR) after maturation while Bcl2 neutrophils are resistant to PCD but maintain PrCR programs. d RNAseq anaylsis of 4 groups of neutrophils, including (1) WT neutrophils from bone marrow (BM), (2) WT neutrophils recruited to peritoneum (PT), (3) MRP8-Bcl2 neutrophils from bone marrow, and (4) MRP8-Bcl2 neutrophils recruited to peritoneum. PT, peritoneal; BM, bone marrow. e Distribution among different cellular pathways (y-axis) of: (blue) 333 genes that are associated with increased susceptibility to PrCR and (red) genes in the human genome. RNAseq analysis was performed on 4 groups of neutrophils, as described in d. RNAseq analysis was used to identify genes upregulated in the maturation process (BM to peritoneum) in both WT and MRP8-Bcl2 mice, which are likely associated with susceptibility to PrCR