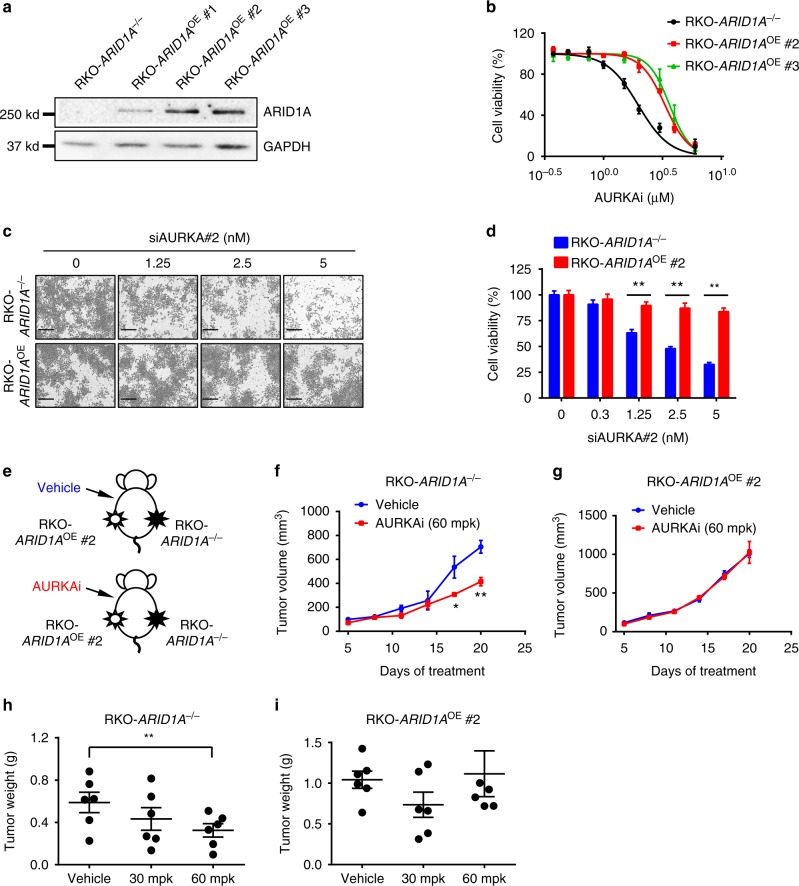
Fig. 3.
In vitro and in vivo synthetic lethality in ARID1A−/− RKO cells by AURKA inhibition. a Stable expression of ARID1A in ARID1A−/− RKO cells using a lentiviral transduction. Three selected ARID1A stable clones are shown. b Dose–response curves of ARID1A−/− parental RKO and ARID1A overexpressing (ARID1AOE) RKO clones treated with AURKAi. Error bars represent s.d. (n = 6) from three independent experiments. Survival curve of ARID1A−/− versus ARID1AOE cell lines, P value < 0.0001, ANOVA. c Synthetic lethality effect of AURKA siRNA (siAURKA#2) on RKO ARID1A isogenic pair. Representative cell images were taken with IncuCyte ZOOM. Scale bars, 300 µm. d Integrated cell density was measured with the IncuCyte ZOOM software as a surrogate for cell viability (right panels). Error bars represent s.d. **P < 0.01, Student’s t test. e Schematic illustration of mouse tumor xenograft experiments with RKO ARID1A isogenic cell pair. f, g Tumor growth curve in nude mice bearing ARID1A−/− RKO (f) or ARID1AOE RKO clone #2 (g) xenografts after injection of vehicle or 60 mg kg−1 (mpk) AURKAi. Error bars represent s.d. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 between vehicle and AURKAi treatment groups (n = 6), Student’s t test. h, i Wet weight measurement of the tumors isolated from mice bearing ARID1A−/− RKO (h) or ARID1AOE RKO clone #2 (i) xenografts at 20 days after injection of vehicle, 30 or 60 mpk AURKAi. Error bars represent s.d. **P < 0.01 between vehicle and 60 mpk AURKAi treatment groups (n = 6), Student’s t test