Figure 4.
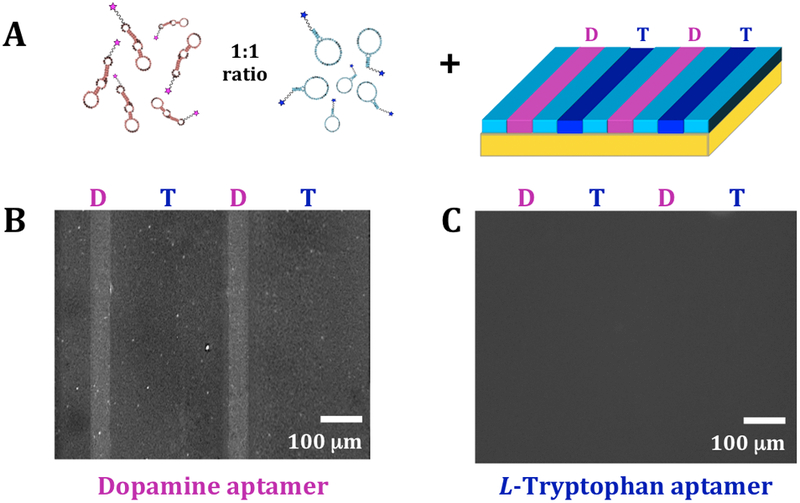
Bi-functionalization of dopamine and L-tryptophan. (A) Schematic (not to scale) of incubation of multiplexed substrates with 1:1 mixtures of dopamine and L-tryptophan aptamers. Representative fluorescence images of the same substrate at (B) an emission wavelength of 605 nm for AlexaFluor® 546 (excitation at 556 nm) to image bound dopamine aptamers and (C) an emission wavelength of 525 nm for AlexaFluor® 488 (excitation at 490 nm) to visualize bound L-tryptophan aptamers. Selective binding was observed for the dopamine aptamer, while negligible binding was detected for the L-tryptophan aptamer (N=3 substrates).
