Fig. 3. Laforin N163D has a similar carbohydrate phosphatase activity and similar ability to bind carbohydrates as wild type.
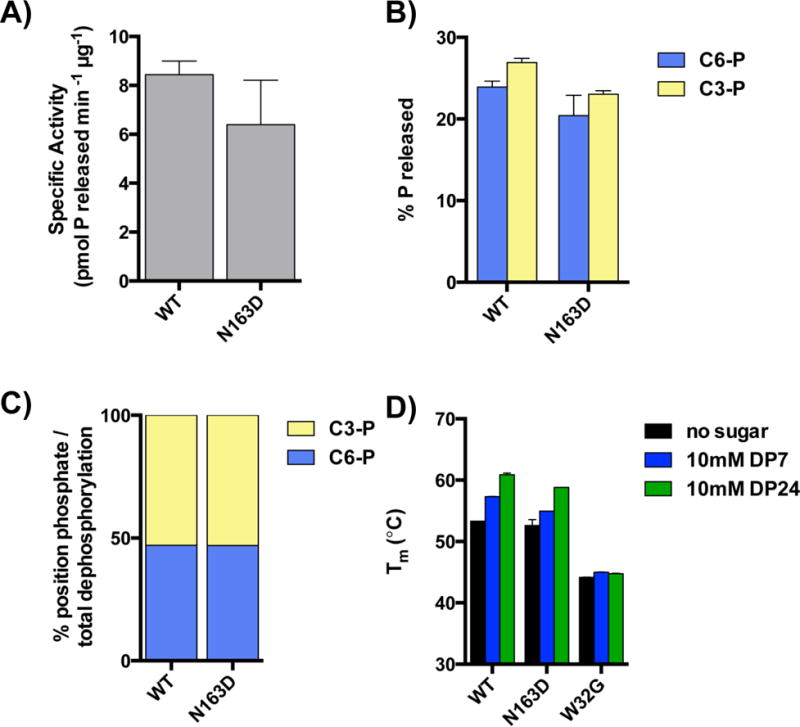
Recombinant laforin wild type and N163D were purified from bacteria. Phosphatase activities of laforin wild type and N163D toward glycogen (A) and substrate radiolabeled at either the C3- or C6-position (B) were assayed as described in Material and Methods. The C3 vs. C6-phosphate release as a percentage of total dephosphorylation is shown in (C). At least three independent samples were analyzed in each case. D) The thermal stability and oligosaccharide binding of purified laforin wild type, N163D and W32G was assessed by differential scanning fluorimetry, as described in Material and Methods. At least three independent samples were analyzed in each case.
