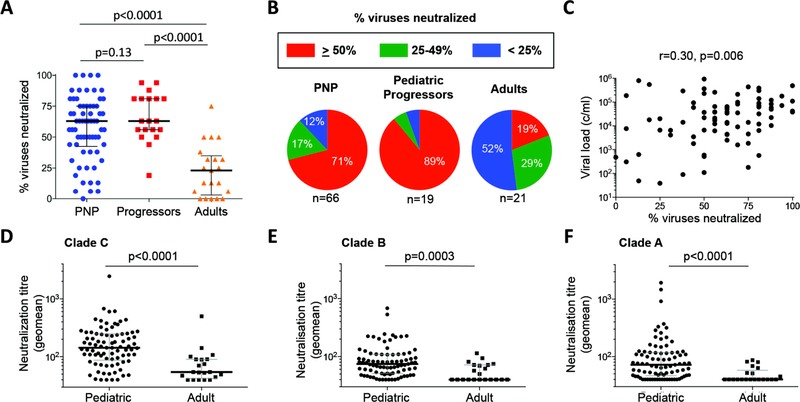
Fig. 4. Neutralization of a panel of 16 tier-2 and −3 subtype C, B and A viruses by pediatric and adult plasma samples.
a: Neutralization breadth in pediatric non-progressors (n=66) and progressors (n=19) compared with adults (n=21). b. The frequency of bnAbs among pediatric non-progressors (median age 6.6yrs, absolute CD4 T-cell count 1,050 cells/mm3, viral load 14,000 copies/ml), pediatric progressors (median age 8.2yrs, absolute CD4 T-cell count 225 cells/mm3, viral load 71,803 copies/ml) and adults (five years after infection, median absolute CD4 T-cell count 449 cells/mm3, viral load 31,200 copies/ml). c. Correlation between viral load and % viruses neutralized among pediatric subjects. P- and r-values were calculated by Spearman rank correlation tests. D–f. Geometric means of neutralization titers for pediatric and adult samples against subtype C (n=6), B (n=6) and A (n=4) viruses. Comparisons between groups were calculated by Mann-Whitney tests.