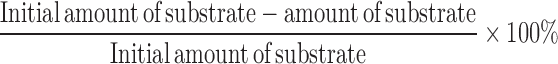Table 3.
Hydrolysis of various substrates by Rhodothermaceae bacterium RA crude enzymes
| Substrate | Spectrophotometric analysisa,b (Unit/mL) | HPLC analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate depletionc (%) | Product formation (µg/mL) | |||||||
| Glucose | C2 | C3 | C4 | Xylose | X2 | |||
| Avicel | 0.000 ± 0.000a | – | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | – | – |
| CMC | 0.411 ± 0.011a | – | 82 | 39 | 18 | 0 | – | – |
| Xylan | 1.428 ± 0.007a | – | – | – | – | – | 1397 | 41 |
| PNPG | 0.019 ± 0.001b | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| PNPX | 0.173 ± 0.001b | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| C2 | – | 16.86 | 318 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C3 | – | 30.06 | 314 | 810 | – | – | – | – |
| C4 | – | 99.28 | 405 | 4928 | 464 | – | – | – |
| C5 | – | 100.00 | 430 | 3042 | 3909 | 0 | – | – |
| C6 | – | 100.00 | 359 | 3354 | 2185 | 229 | – | – |
| C7 | – | 100.00 | 306 | 1230 | 494 | 58 | – | – |
| X2 | – | 95.06 | – | – | – | – | 4233 | – |
| X3 | – | 100.00 | – | – | – | – | 3958 | 419 |
| X4 | – | 100.00 | – | – | – | – | 3786 | 368 |
| X5 | – | 100.00 | – | – | – | – | 3392 | 240 |
| X6 | – | 100.00 | – | – | – | – | 3276 | 193 |
– indicates not available. C2–C7 indicate cellobiose to celloheptaose, respectively. X2–X6 indicate xylobiose to xylohexaose, respectively
aReading taken at wavelength 540 nm (DNS assay). One unit (U) of enzyme activity was defined as the enzyme amount that can liberate 1 µmol of reducing sugar per min per mL under assay condition
bReading taken at wavelength 405 nm. One unit (U) of enzyme activity was defined as the enzyme amount that can liberate 1 µmol of p-nitrophenol per min per mL under assay condition
cCalculated using formula: