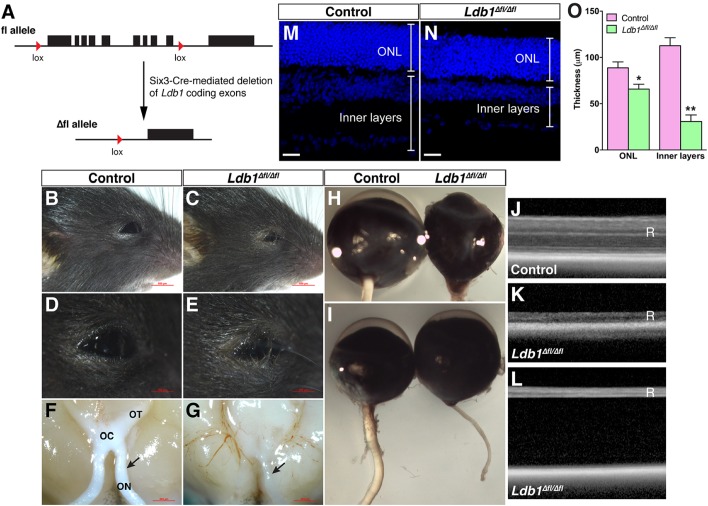
FIGURE 3.
Conditional knockout of Ldb1 causes defective eye development. (A) The cartoon illustrates that Six3-Cre-mediated recombination removes most of the Ldb1 coding exons. (B–E) Loss of Ldb1 often results in a microphthalmia phenotype. (F,G) Atrophic optic nerve, optic chiasm and optic tract in Ldb1Δfl/Δfl animals. (H,I) Optic nerve hypoplasia and incomplete penetrant microphthalmia phenotype in Ldb1Δfl/Δfl mice. (J,K) OCT images show that the retina gets much thinner in the mutant mouse. (L) OCT image showing that the retina gets detached from the pigment epithelium layer in a severely affected mutant mouse. (M–O) The thickness of the ONL and inner layers of wildtype and Ldb1 mutant retinas, visualized by nuclear DAPI labeling, was quantified at P21. Each histogram in O represents the mean ± SD for 3 animals. ∗p < 0.01; ∗∗p < 0.0005. OC, optic chiasm; ON, optic nerve; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OT, optic tract; R, retina. Scale bar: (M,N) 20 μm.