FIGURE 5.
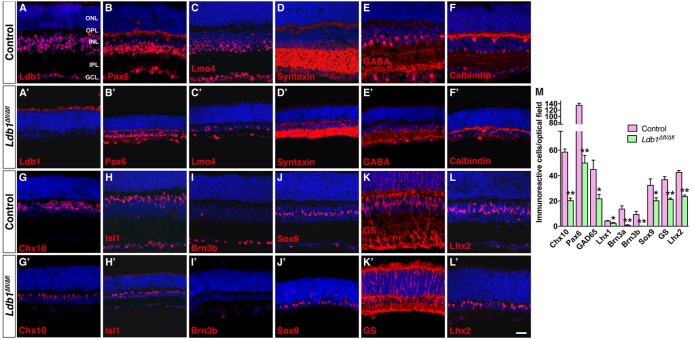
Conditional knockout of Ldb1 causes loss of all non-photoreceptor cell types. (A,A’) Ldb1 immunoreactivity was near completely abolished in the mutant retina. (B,B’) Immunoreactivity for Pax6, a cell marker for amacrine, horizontal and ganglion cells, was reduced in the mutant. (C,C) The Ldb1 binding cofactor Lmo4, usually present in nearly all major cell types in the INL and GCL, was decreased in the mutant. (D,D’) Syntaxin, a marker for all amacrine cells, was dramatically reduced in the mutant. (E,E’) GABA immunoreactive amacrine cells were diminished in the mutant. (F,F’) Calbindin is expressed in all horizontal cells and some amacrine cells in the wildtype retina. These cells were greatly reduced in the mutant. (G,G’) Chx10+ bipolar cells were vastly decreased in the mutant. (H,H’) Isl1 is present in ON-bipolar, cholinergic amacrine, and ganglion cells. These cells especially ganglion cells were drastically reduced in the mutant. (I,I’) Brn3b+ ganglion cells nearly disappeared in the Ldb1 mutant. (J–L,J’–L’) Müller cells immunoreactive for Sox9, GS or Lhx2 were decreased in the mutant. (M) Quantification of some typical cell markers in control and Ldb1 mutant retinas. Each histogram represents the mean ± SD for three retinas. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.005. All retinal sections were counterstained with nuclear DAPI. GCL, ganglion cell layer; GS, glutamine synthetase; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer. Scale bar: (A–L,A’–L’) 20 μm.