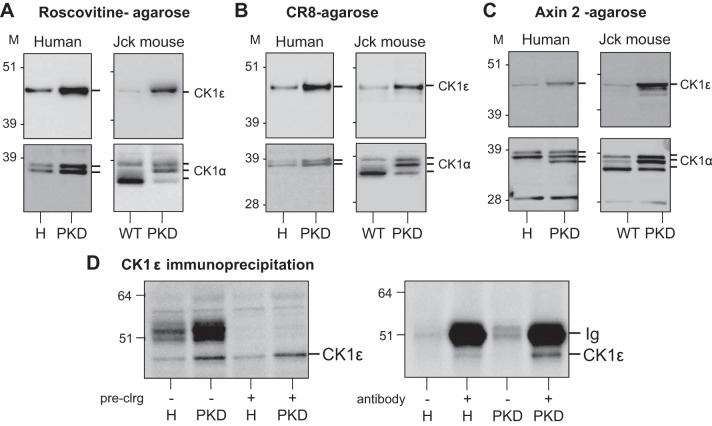
Fig. 3.
CK1ε is overexpressed in polycystic kidneys. Roscovitine and CR8-binding proteins in healthy and polycystic kidneys. A–C: equal amounts of extracts, prepared from human (left) and jck mouse (right) healthy (H) and polycystic [polycystic kidney disease (PKD)] kidneys, were loaded on roscovitine (A), CR8 (B), or axin 2 (C) beads. After extensive washing, the bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by WB with antibodies directed against CK1ε or CK1α. M, molecular weight markers. D: increased CK1ε in PKD vs. healthy kidneys is also seen following immunoprecipitation. Left: extracts of H and PKD kidneys (jck) were first precleared or not on protein G agarose, and total proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by WB with anti-CK1ε. Note the increased expression of CK1ε maintained following preclearing. Right: CK1ε was next immunoprecipitated from precleared H and PKD kidney extracts and detected by WB. Note the absence of CK1ε in the absence of antibodies and the increased expression of immunopurified CK1ε in PKD vs. H kidneys.