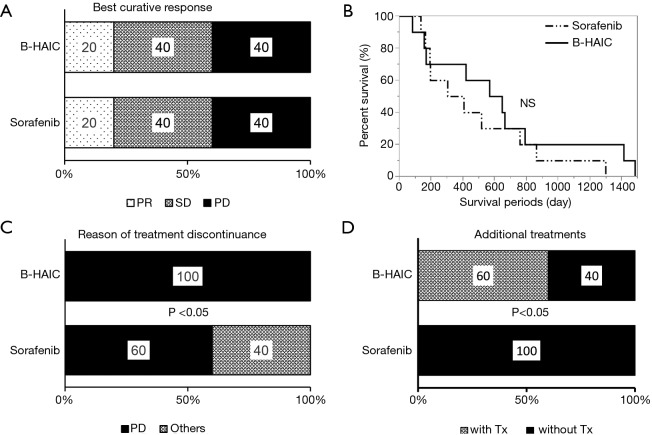
Figure 4.
Chemopreventive effect of B-HAIC and sorafenib on advanced HCC with intravascular invasion. (A) Both of the B-HAIC group and the sorafenib group included the same populations of partial responder, stable disease, and progressive disease, respectively; (B) Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival of patients treated with B-HAIC (solid line) and sorafenib (dashed line); (C) 40% of patients treated with sorafenib discontinued the treatment because of adverse events, whereas no patients terminated B-HAIC treatment due to adverse events; (D) the B-HAIC group patients exhibited a higher rate of additional chemotherapy than the sorafenib group. B-HAIC, bi-monthly hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; NS, non-significant.