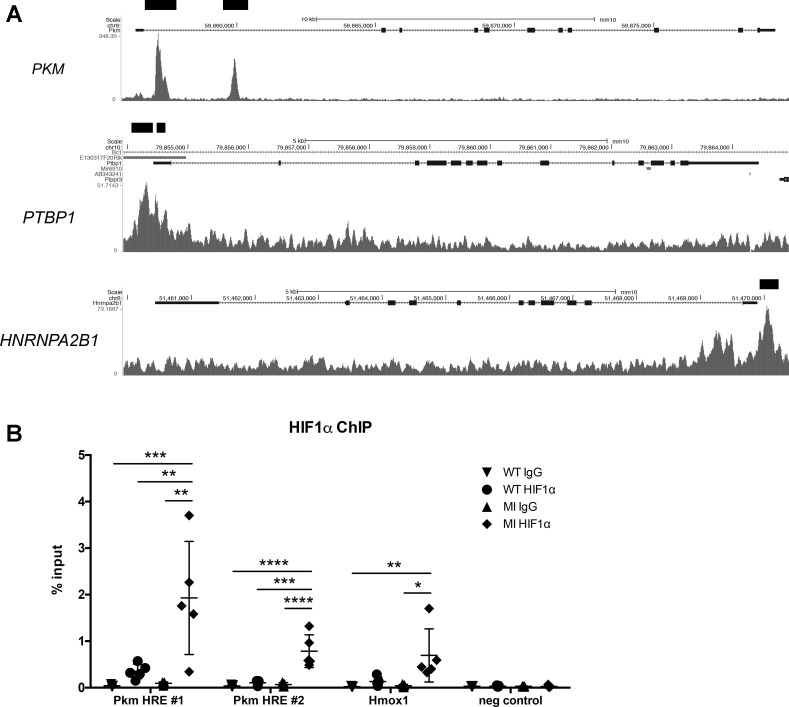
Fig. 8.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP) analysis of HIF1 binding to PKM (and related splicing factors). A: analysis of HIF1 binding sites in embryonic mouse hearts by ChIP-seq from Guimarães-Camboa et al. (12). Genome browser plots of PKM, PTBP1, and HNRNPA2B1 show signals from HIF1α-bound sequences. Black bars denote statistically significant peaks. B: semiquantitative PCR analysis of ChIP DNA using an HIF1α antibody on naïve wild-type (WT) and ischemic heart tissue 1 day after MI (MI). HIF1α showed increased binding at hypoxia response element (HRE) sites compared with both WT and IgG controls for Pkm and Hmox1, a known HIF1 target, while no binding was detected in the negative control, a site with no transcriptional activity. n = 5 for each group. Data shown as % of total input DNA and displayed with means ± SD. Statistical significance determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons or Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.