FIGURE 1.
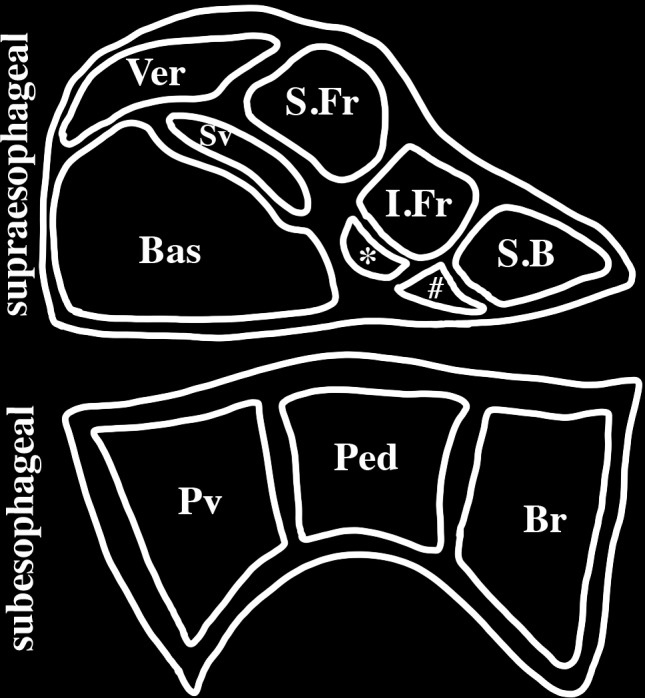
Schematic representation of a mid-sagittal section of an octopus brain. The brain is encased in a cartilaginous capsule and consists of two principal regions: the supraesophageal region lying above the esophagus and the subesophageal region lying below the esophagus. The principal lobes of the midline supraesophageal region consists of the vertical (V), subvertical (Sv), superior frontal (S.Fr), inferior frontal (I.frontal), superior buccal (S.B), posterior buccal (#), subfrontal (∗) and basal (Bas) lobes. The inferior frontal consists of a median lobe (shown here) and a lateral lobe (not shown here) that is located lateral to the midline. The subesophageal brain is partitioned into three lobes: brachial (Br) which gives rise to the brachial nerves to the arms, pedal (Ped) and palliovisceral (Pv) lobes.
