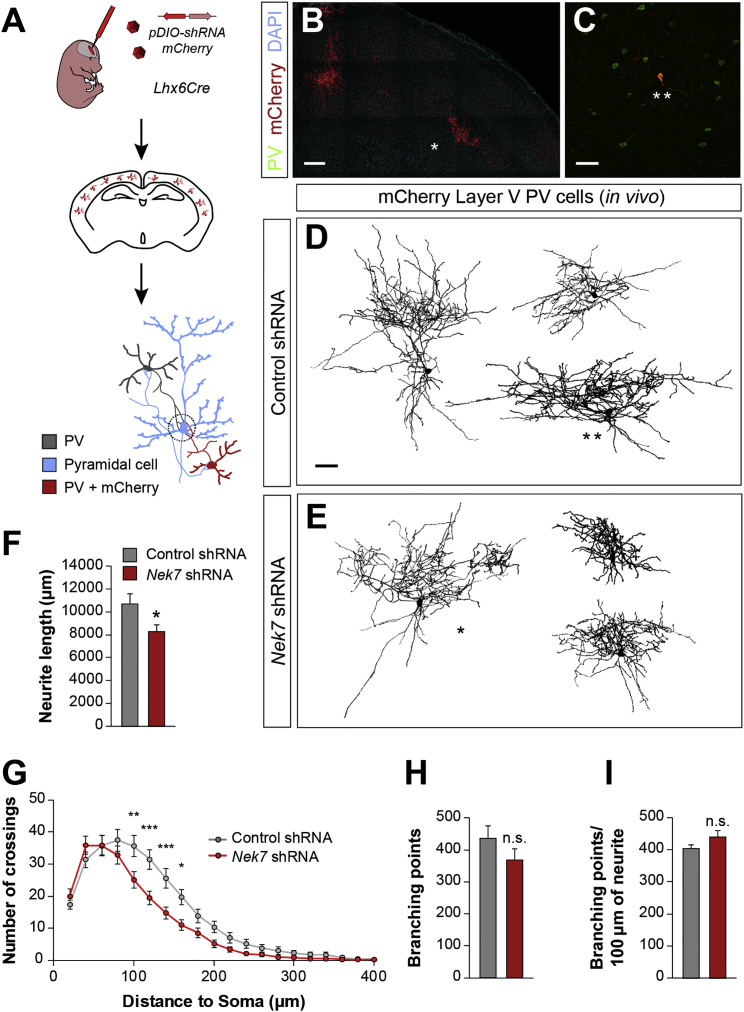
Figure 6.
Loss of NEK7 Causes Abnormal PV+ Neuronal Morphology In Vivo
(A) Schematic of experimental design. Cre-dependent AAVs expressing shRNA and the fluorescent marker mCherry were injected in E15.5 Lhx6Cre mice in vivo.
(B and C) Targeted mCherry+ interneurons (B) that were PV+ (C) were selected for the analysis.
(D and E) Confocal Z projections of PV+ interneurons expressing control shRNA (D) and Nek7 shRNA (E) reported by mCherry. The cells were automatically reconstructed and masked in black from layer V of somatosensory cortex at P21.
(F–I) Average of total neurite length (F), Sholl analysis (G), total branching points (H), and branching points per 100 μm of neurite (I) of control shRNA (n = 30 PV+ neurons, from 10 mice) and Nek7 shRNA (n = 27 PV+ neurons, from 8 mice) infected neurons. One-way ANOVA (F, H, and I) and two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (G).
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001; n.s., not significant. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Scale bars represent 200 μm (B) and 50 μm (C–E). See also Figure S6.