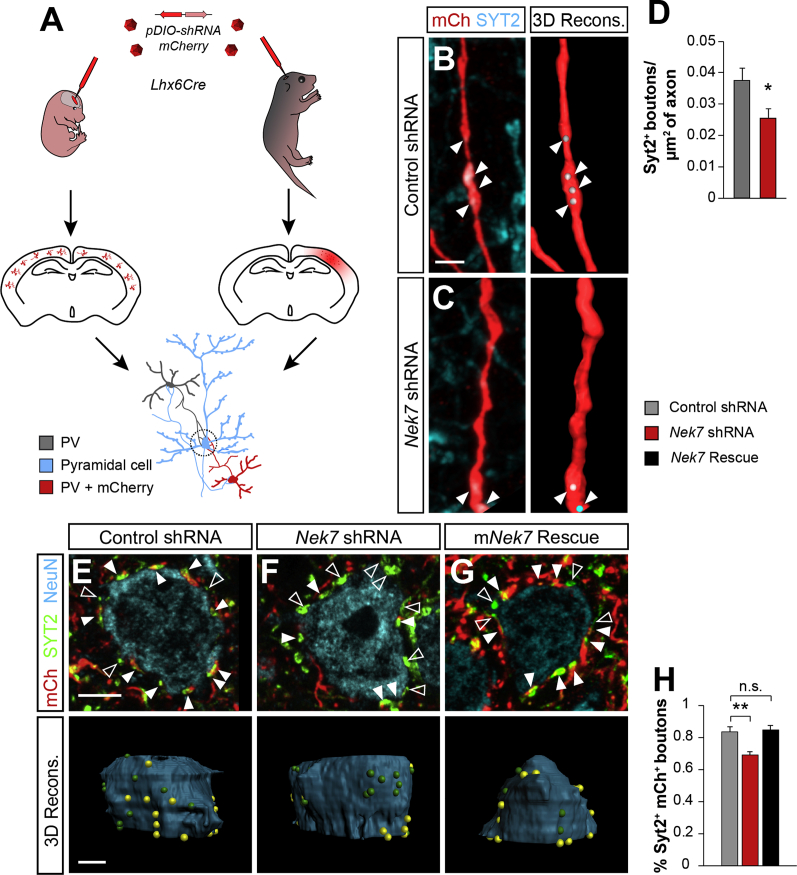
Figure 7.
Nek7 Knockdown Decreases PV+ Interneuron Outputs
(A) Schematic of the experimental design. Cre-dependent virus expressing shRNA and the fluorescent marker mCherry were injected in E15.5 (left) and P3 (right) Lhx6Cre mice in vivo. Boutons co-stained with SYT2 and mCherry were quantified either inside PV+ arbors or onto NeuN+ somata.
(B and C) Confocal Z projections and Imaris 3D reconstructions showing control shRNA (B) and Nek7 shRNA (C) infected PV+ cells expressing mCherry (red) in axons containing SYT2+ boutons (blue).
(D) SYT2+ bouton density per unit area of neurite comparing control shRNA (n = 24 PV+ neurons from four mice) and Nek7 shRNA (n = 22 PV+ neurons from six mice). Student’s t test.
(E–G) Confocal images and 3D Imaris reconstructions showing mCherry+ (red), SYT2+ (green) synaptic boutons from infected PV+ cells expressing control shRNA (E), Nek7 shRNA (F), and Nek7 shRNA with mNek7 for rescue (G) contacting pyramidal cells NeuN+ (blue). SYT2+ mCherry+ (filled arrowheads, yellow spheres), SYT2+ mCherry− (open arrowheads, green spheres).
(H) Percentage of SYT2+ mCherry+ somatic boutons contacting the pyramidal cells normalized to the percentage of PV+ cells infected in the area, comparing shRNA (n = 182 PV+ neurons from seven mice), Nek7 shRNA (n = 200 pyramidal cells from six mice), and mNek7 (n = 109 pyramidal cells from four mice). Kruskal-Wallis test, pairwise comparisons.
∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01; n.s., not significant. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Scale bars represent 2 μm (B and C) and 5 μm (E–G). See also Figure S6.