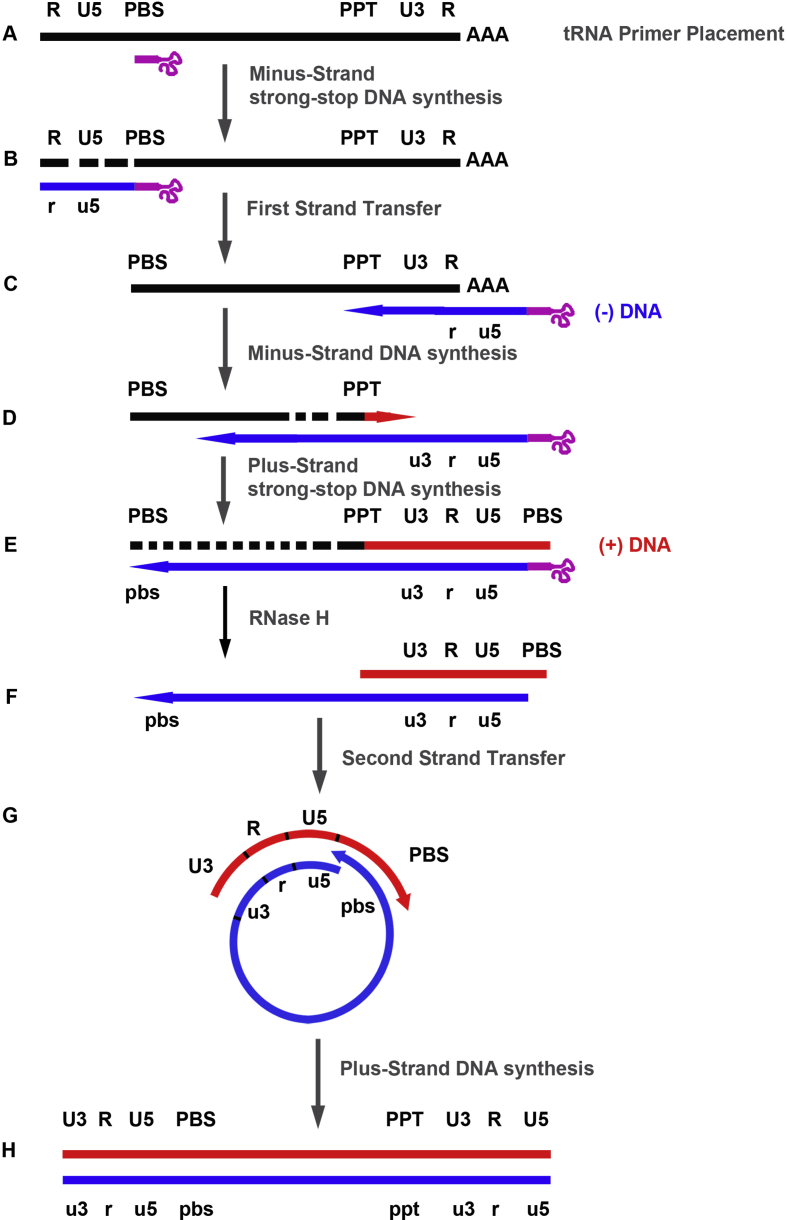
Fig. 2.
Reverse transcription of the retroviral RNA genome. A) The 3′-end of a cellular tRNA (pink line) is annealed to the PBS region of the retroviral RNA (black line). B) Minus-strand DNA (blue line) synthesis is initiated from the tRNA primer to the 5′-end of genome; this product is named minus-strand strong-stop DNA ((−) ssDNA); the genomic RNA is degraded by the RNase H activity of RT. C) The (−) ssDNA is transferred to the 3′-end of the genomic RNA. D) After the first strand transfer, elongation of minus-strand DNA and RNase H degradation continue; plus-strand DNA (red line) synthesis is initiated from a polypurine tract (PPT) sequence that is resistant to RNase H cleavage. E) Elongation of the two DNA strands until the PBS sequences. F) Retroviral RNA, the tRNA and PPT primers are degraded by the RNase H activity of RT. G) The second strand transfer is mediated by base pairing of the complementary PBS sequences at the 3′-ends of minus-strand DNA and plus-strand strong-stop DNA. H) Elongation of minus- and plus-strand DNAs, resulting in a linear double-stranded DNA with a long terminal repeat (U3 R U5) at each end.