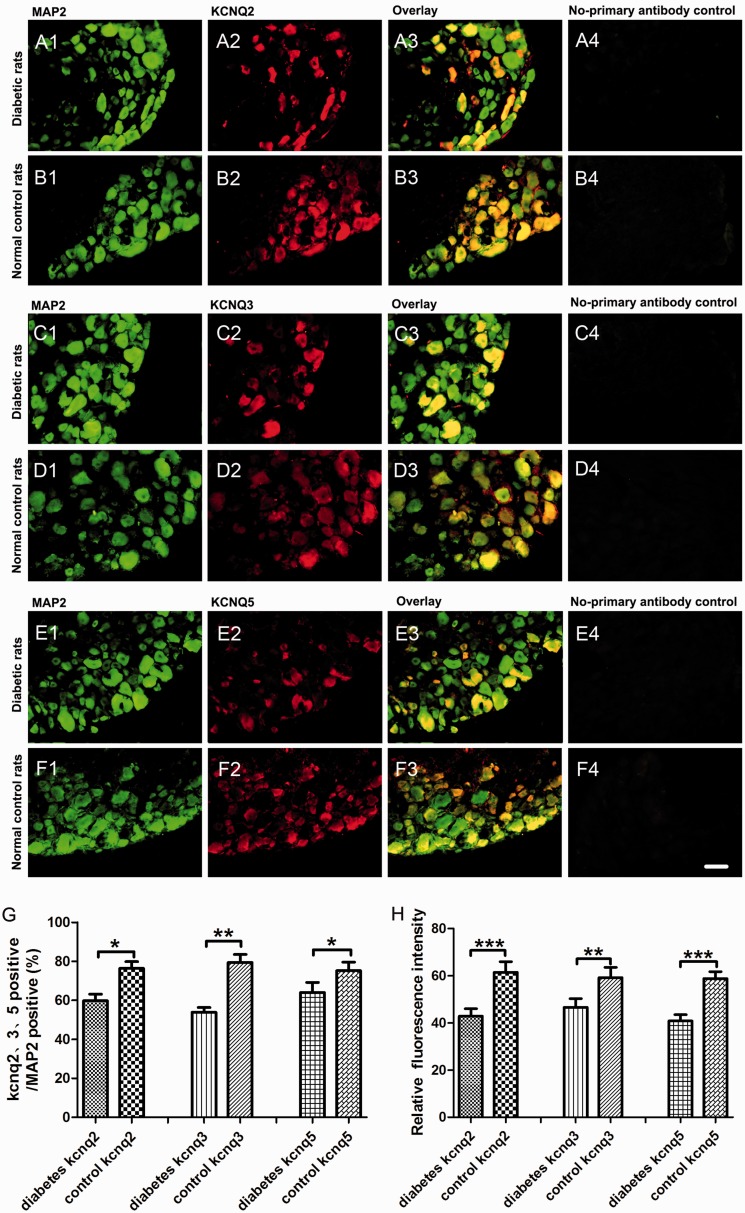
Figure 3.
KCNQ2/3/5 channels expression in situ in DRG neurons. Double fluorescent labeling revealed that the percentage of KCNQ2/3/5-positive neurons of total neurons (MAP2-positive neurons) decreased dramatically in DRG of diabetic neuropathic pain rats compared to normal control rats. (A1–A4) The examples of MAP2-positive (green), KCNQ2-positive (red) DRG neurons, overlay, and no-primary antibody control in diabetic rats. (B1–B4) The examples of MAP2-positive (green), KCNQ2-positive (red) DRG neurons, overlay, and no-primary antibody control in normal control rats. (C1–C4) The examples of MAP2-positive (green), KCNQ3-positive (red) DRG neurons, overlay, and no-primary antibody control in diabetic rats. (D1–D4) The examples of MAP2-positive (green), KCNQ3-positive (red) DRG neurons, overlay, and no-primary antibody control in normal control rats. (E1–E4) The examples of MAP2-positive (green), KCNQ5-positive (red) DRG neurons, overlay, and no-primary antibody control in diabetic rats. (F1–F4) The examples of MAP2-positive (green), KCNQ5-positive (red) DRG neurons, overlay, and no-primary antibody control in normal control rats. (G) The quantitative analysis of the proportion of KCNQ2/3/5-positive (red) to MAP2-positive (green) DRG neurons. (h) The quantitative analysis of KCNQ2/3/5 channels relative immunofluorescence intensity to MAP2 immunofluorescence intensity. Scale bar = 50 μm. Bar graphs with error bars represent mean ± SEM, n = 5, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, paired Student’s t test. MAP2: microtubule-associated protein 2.