Figure 1.
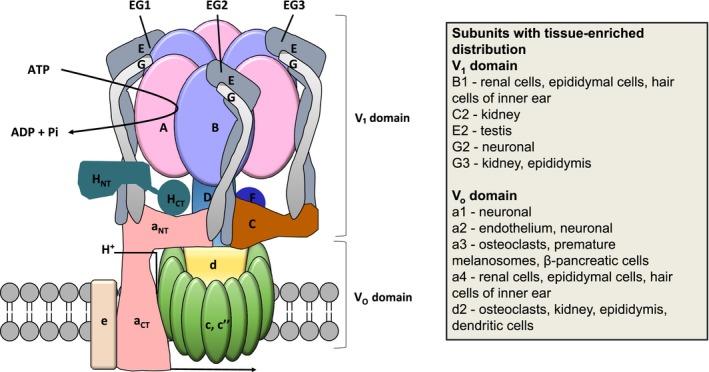
V‐ATPase structure. The V1 domain contains the A3B3 catalytic hexamer, the peripheral stalk made up of subunits E, G, C, and H, and D and F of the central rotor. ATP hydrolysis occurs in the A3B3 catalytic hexamer and the energy generated is used to drive the rotary mechanism. The Vo domain is integrated into the membrane and is responsible for proton translocation; it consists of subunits a, d, e and the proteolipid ring made up of c and c″. Many of the subunits are expressed in the form of multiple isoforms; the tissue enriched localization of some of the important isoforms is shown
