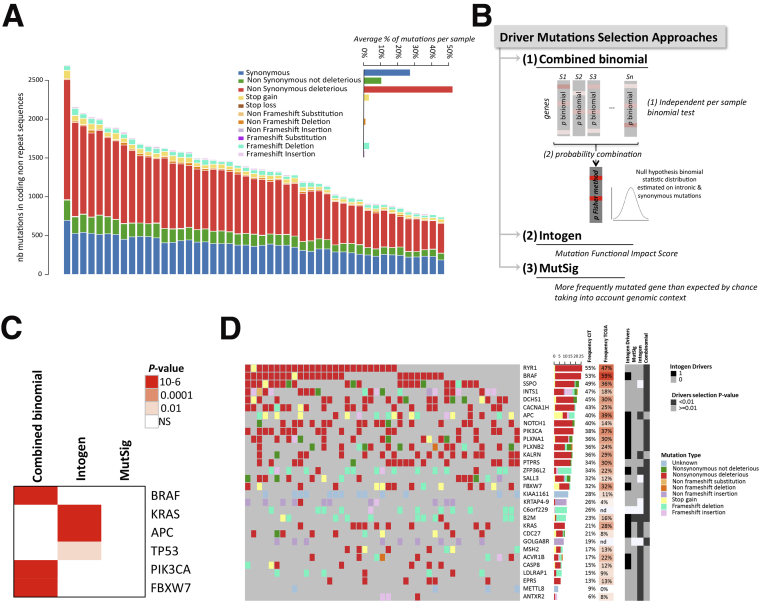
Figure 3.
Identification of candidate driver genes with mutations in NR sequences. (A) Distribution of mutation types in coding NR regions according to their functional impact (annotation tool Annovar). The functional impact was based on several methods, with a mutation considered as deleterious if at least 1 of those methods estimated it to be deleterious. The average percentage of each mutation type per sample is shown in the inset. (B) Schematic representation of the 3 methods (MutSigCV, Intogen, combined binomial) used in this study to identify driver mutations (see the Methods section for details). (C) Heatmap of the significance (q values) of mutated genes commonly described for their functional impact in MSI CRC using Intogen, combined binomial, and MutSigCV analyses. (D) Oncoprint representation of mutations in coding NR sequences within each sample for the 25 top significantly mutated genes (indicated in darker grey for each approach on the side annotation heatmap) and for the 5 significant genes considered as driver genes by Intogen (indicated in black on the side annotation heatmap) across samples. Top and side bar plots indicate the percentage of each type of mutation within the sample and within the gene, respectively.