Fig. 3. Paradoxical reaction in a young child with TBM.
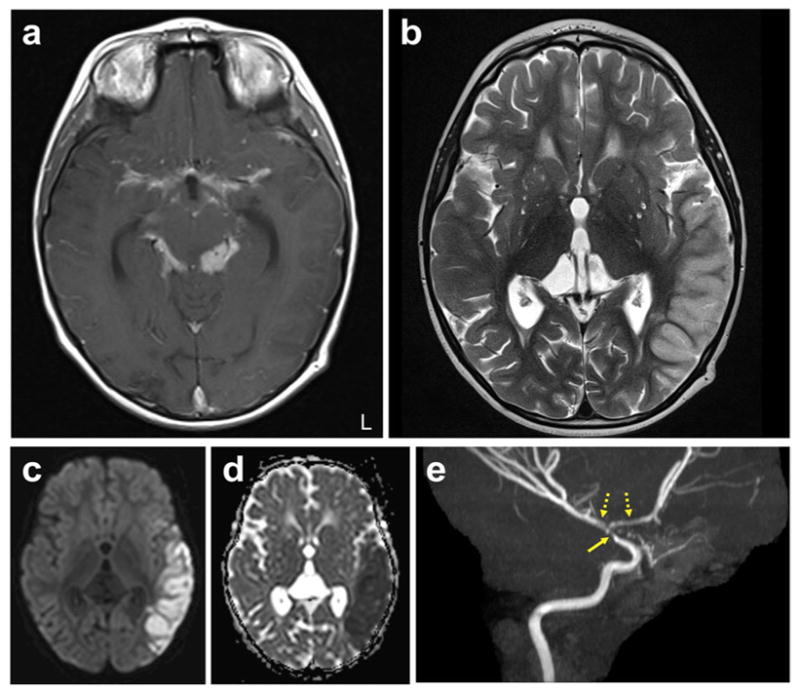
Brain MRI of a four-year-old, HIV-negative child with microbiologically confirmed TBM presenting with paradoxical reaction ten weeks after initiation of TB treatment. a–e, Representative enhanced T1-weighted (a) and T2-weighted (b) images, diffuse weighted imaging (DWI) (c), ADC (apparent diffusion coefficient) map (d) and MR angiography (maximum-intensity projection) (e) are shown. T2 hyperintensity involving the left temporal cortex is seen, with corresponding increased signal on DWI and decreased signal on ADC, consistent with left middle cerebral artery distribution acute stroke. The enhanced T1-weighted image shows extensive thick basilar meningeal enhancement. Narrowing of the distal left internal carotid artery (solid arrow) with irregularity and narrowing of the M1 and A1 segments (dashed arrows) are noted on the angiogram. Corticosteroids were reinitiated at this time, and the child improved considerably, with sustained improvement noted at follow-up many months later. L, left. (Credit: unpublished data, S.K.J. The author is in compliance with Johns Hopkins School of Medicine institutional policy regarding single-case deidentified patient data.)
