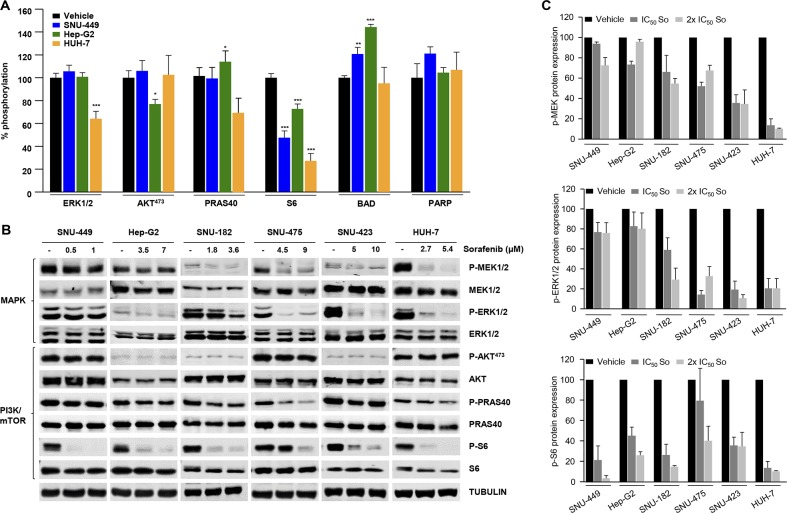
Figure 2. Mechanistic effects of sorafenib in a panel of HCC cell lines.
(A) Intracellular signaling array of SNU-449, Hep-G2 and HUH-7 cells starved and treated for 1h with their IC50 concentration of Sorafenib. (B) Western blotting analyses of SNU-449, Hep-G2, SNU-182, SNU-475, SNU-423 and HUH-7 cells starved and treated for 1h with control vehicle (−) and the IC50 and 2x IC50 concentrations of sorafenib, as indicated. Cell lysates were incubated with P-MEK1/2, MEK1/2, P-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, P-AKT473, AKT, P-PRAS40, PRAS40, P-S6, S6, and α-tubulin antibodies. (C) P-MEK, P-ERK1/2 and P-S6 relative to MEK, ERK1/2 and S6 protein expression in HCC cell lines treated with control vehicle, the IC50, and 2 x IC50 concentrations of sorafenib. Error bars show SEM. * compared with the control vehicle (* P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).