FIGURE 4.
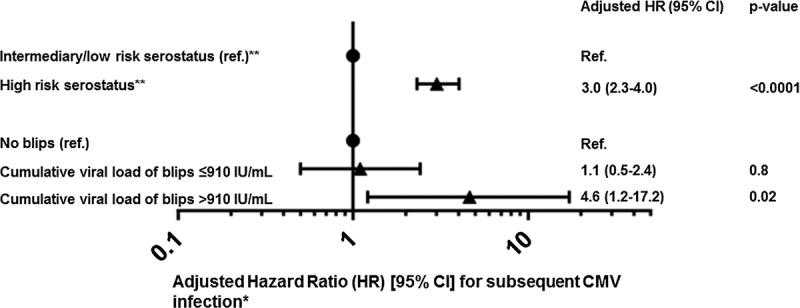
Forest plot of HR [95% CI] for a first CMV infection after transplantation. *Time dependent variables were updated accordingly, and death was included as a competing risk. The model also included age, sex, calendar year, and adjusted for type of transplantation (kidney, liver, heart, lung, myeloablative conditioning transplantation, nonmyeloablative conditioning and umbilical cord blood transplantations). Compared with kidney recipients, lung and umbilical cord blood transplantation recipients had an increased HR of subsequent CMV infection (lung (HR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.03-2.3; P = 0.03) and umbilical blood cord (HR, 4.3; 95% CI, 1.6-12.0; P = 0.004) respectively. **For solid organ transplantation recipients CMV IgG D+/R- is associated with high risk of CMV infection, while D-/R+ is associated with low risk. Among bone marrow transplant recipients, D-/R+ is associated with a high risk of CMV infection, whereas D+/R- is associated with a low risk. For both types of transplantation, D+/R+ is associated with intermediary risk of CMV infection.
